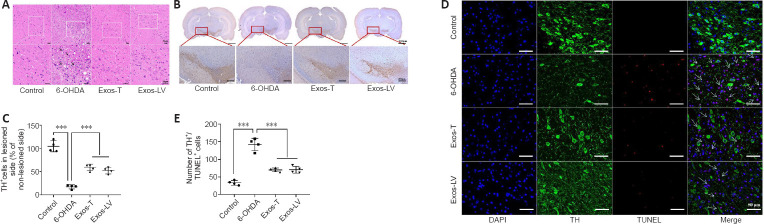
Figure 3.
HucMSC-Exos reduces the damage to DA neuron in the substantia nigra of PD model rats.
(A) HE staining. Arrows indicate areas where neuronal loss and morphological changes were observed. The rectangle indicates the location of the damage. Compared with the control group, cells in the 6-OHDA group were disarranged, some neurons were shrunk, and severe structural damage could be seen. These pathological changes were not apparent in the Exos-T and Exos-LV groups. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) Representative TH immunohistochemical staining of the substantia nigra. The left side was the damaged side, and the right side was the undamaged side. Scale bars: 2000 μm in the first row, 200 μm in the second row. (C) TH+ cells. (D) TH (green) and TUNEL (red) immunoreactivity in neurons in the substantia nigra. Blue indicates DAPI-stained nuclei. Scale bars: 50 μm. (E) Quantification of TUNEL+ and TH+ cells. Arrows indicated neurons positive for TUNEL staining and TH expression, and the box represents the enlarged area. All data shown in C and E are shown as the mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001 (n = 4; one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test). Exos-T and Exos-LV indicate 6-OHDA-induced PD models treated with Exos injection through the tail or lateral ventricle, respectively. 6-OHDA: 6-Hydroxydopamine; DA: dopamine; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Exos: exosomes; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; hucMSCs-Exos: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes; PD: Parkinson’s disease; TH: tyrosine hydroxylase; TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dUTP Nick-end labeling.