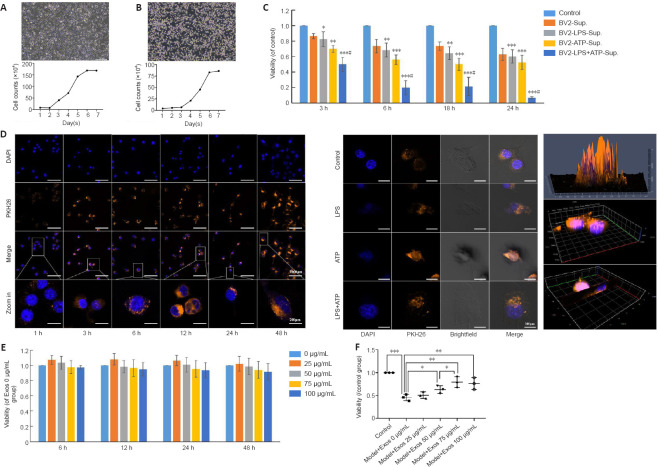
Figure 5.
HucMSC-Exos are taken up by BV2 cells and mitigate the deleterious effect on SH-SY5Y cell viability caused by growth in conditioned medium from BV2 cells stimulated with LPS.
(A, B) Morphology and growth curves of SH-SY5Y and BV2 cells. (C) Conditioned medium from BV2 cells stimulated with LPS + ATP reduced SH-SY5Y cell viability. Scale bars: 200 μm. (D) Uptake of Exos by normal BV2 cells at different time periods (left) (scale bars: 100 μm in DAPI, PKH26, and merge rows and 20 μm in the zoomed in row) and by BV2 cells stimulated with LPS and ATP at 24 hours (middle) (scale bars: 20 μm), as determined by 2.5D (upper) and 3D (middle and bottom) confocal microscopy of Exos in normal BV2 cells at 3 hours (right). Bright field and scanning microscopy showed that Exos entered the BV2 cells. Blue indicates the nuclei, and orange indicates the Exos. The box indicates the enlarged area. (E) The concentration-time curve of the effect of Exos on BV2 cell viability. The cell viability did not change significantly (P > 0.05) when treated with 0 to 100 μg/mL Exos for 6, 12, 24, or 48 hours. (F) The effect of conditioned medium from BV2 cells pretreated with different concentrations of Exos for 6 hours and stimulated with LPS and ATP on SH-SY5Y cell viability. Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 assay. Three wells were assayed for each group, and the experiment was repeated three times. All data were shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. control group, #P < 0.05, vs. BV-sup group (n = 3, one-way analysis of variance followed by the least significant difference test). ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; CCK8: Cell Counting Kit-8; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Exos: exosomes; hucMSCs-Exos: human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes; LPS: lipopolysaccharide.