Figure 1.
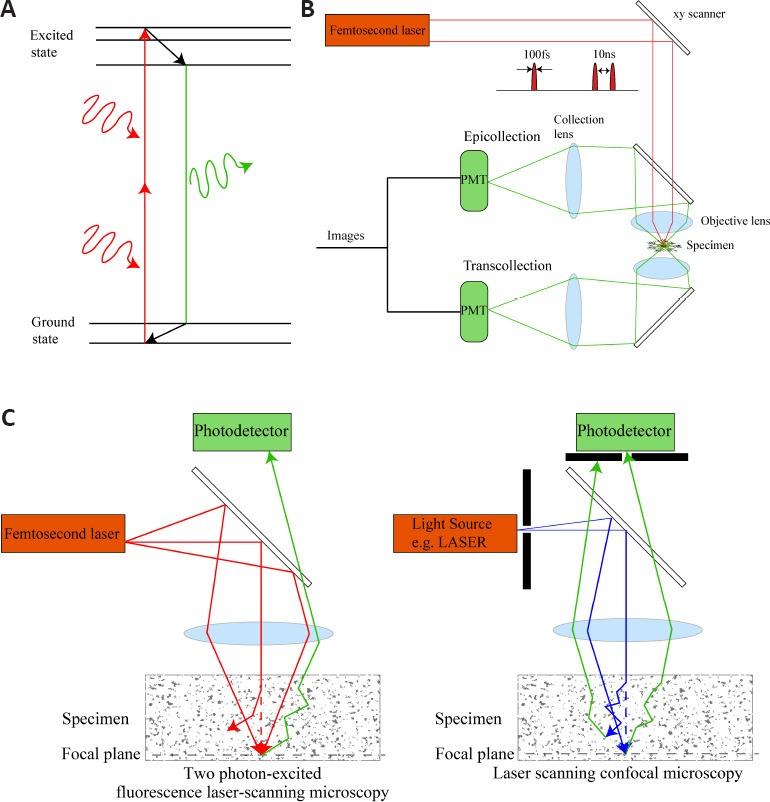
Simplified imaging strategy of 2PLSM and comparison of 2PLSM with laser scanning confocal microscopy.
(A) A simplified Jablonski diagram of the imaging process for 2PLSM. The two long-wavelength photons are used to simultaneously excite one fluorescent probe from the ground state to an excited electron state. (B) A simplified schematic of a 2PLSM with epifluorescence and transfluorescence collection. A femtosecond pulsed laser with a pulse width of 100 fs and a repetition period of 10 ns will excite light with a high density of photons, increasing the chance of excitation on the focal plane while reducing tissue damage. For intravital imaging, only epifluorescence collection is permitted. PMT refers to photomultiplier tube, used to detect weak photon signals and multiply them, converting them into electrical signals and finally forming images. (C) Different imaging strategies for scattered specimens using 2PLSM and laser scanning confocal microscopy. In 2PLSM, the paths of two ballistic photons and one scattered photon are shown (red lines). The energy of the scattered photon away from the focal plane is too low to excite fluorescent molecules. In laser scanning confocal microscopy, the paths of one ballistic photon and one scattered photon are shown (blue lines). The corresponding fluorescent photons are shown (green lines). The laser scanning confocal microscopy uses the pinhole to filter the off-focus plane fluorescence. However, fluorescent photons on the focal plane may also be scattered and filtered by the pinhole. 2PLSM: Two photon-excited fluorescence laser-scanning microscopy.
