FIGURE 2.
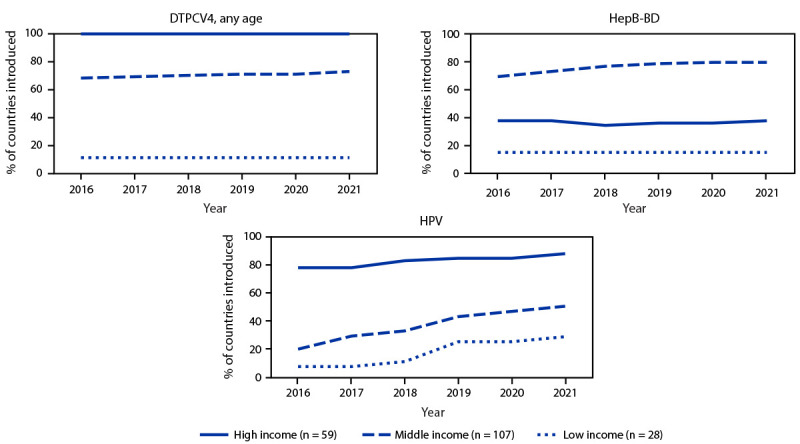
Percentage of countries that introduced selected World Health Organization–recommended vaccines* into their national immunization schedule, by income status† — worldwide, 2016–2021
Abbreviations: DTPCV4 = first booster dose of diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis–containing vaccine; HepB-BD = hepatitis B vaccine birth dose; HPV = human papillomavirus vaccine; USD = U.S. dollars.
* Vaccines with lowest introduction in low-income countries' national immunization schedules as of 2021. HepB-BD indicates the introduction of universal HepB-BD into the national immunization schedule. In addition, 24 countries had implemented HepB-BD selective introduction, of which 22 were high-income and two were middle-income countries.
† Country income categories were defined using the 2022 World Bank income classification except for Cook Islands, Niue, and Venezuela. Cook Islands is classified as high-income and Niue is classified as middle-income based on Central Intelligence Agency classification (https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/). Venezuela is classified as middle-income based on that country’s most recent World Bank classification (2019). Gross national income: low income <1,085 USD; middle income = 1,086–13,205 USD; and high income >13,205 USD.
