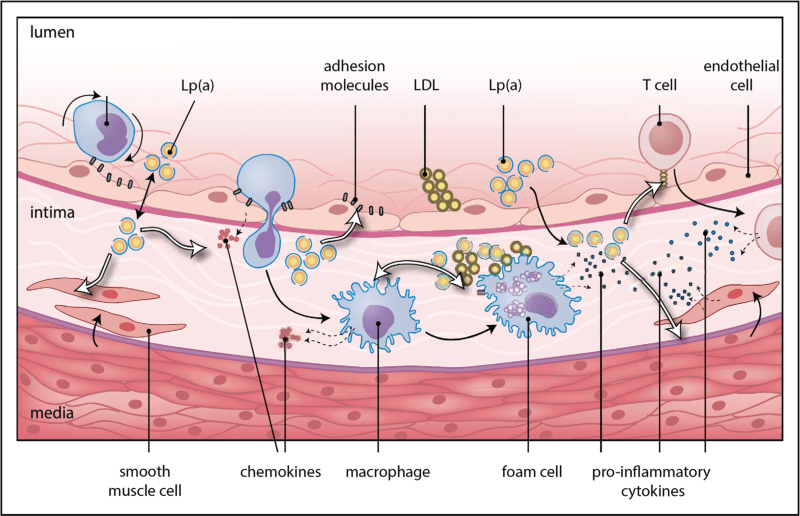
FIGURE 2.
High lipoprotein(a) results in atherosclerosis. Simplified pathophysiology of Lp(a) in the arterial wall. The potential antifibrinolytic properties of Lp(a) due to its structural similarity to plasminogen are not shown in this figure. LDL, low-density lipoprotein; Lp(a), lipoprotein(a). Adapted and reproduced with permission from Nurmohamed et al. Focus Vasculair 2021, Prelum.