Fig. 1. Attentional bias measured by reward-driven attentional bias (RDAB) task.
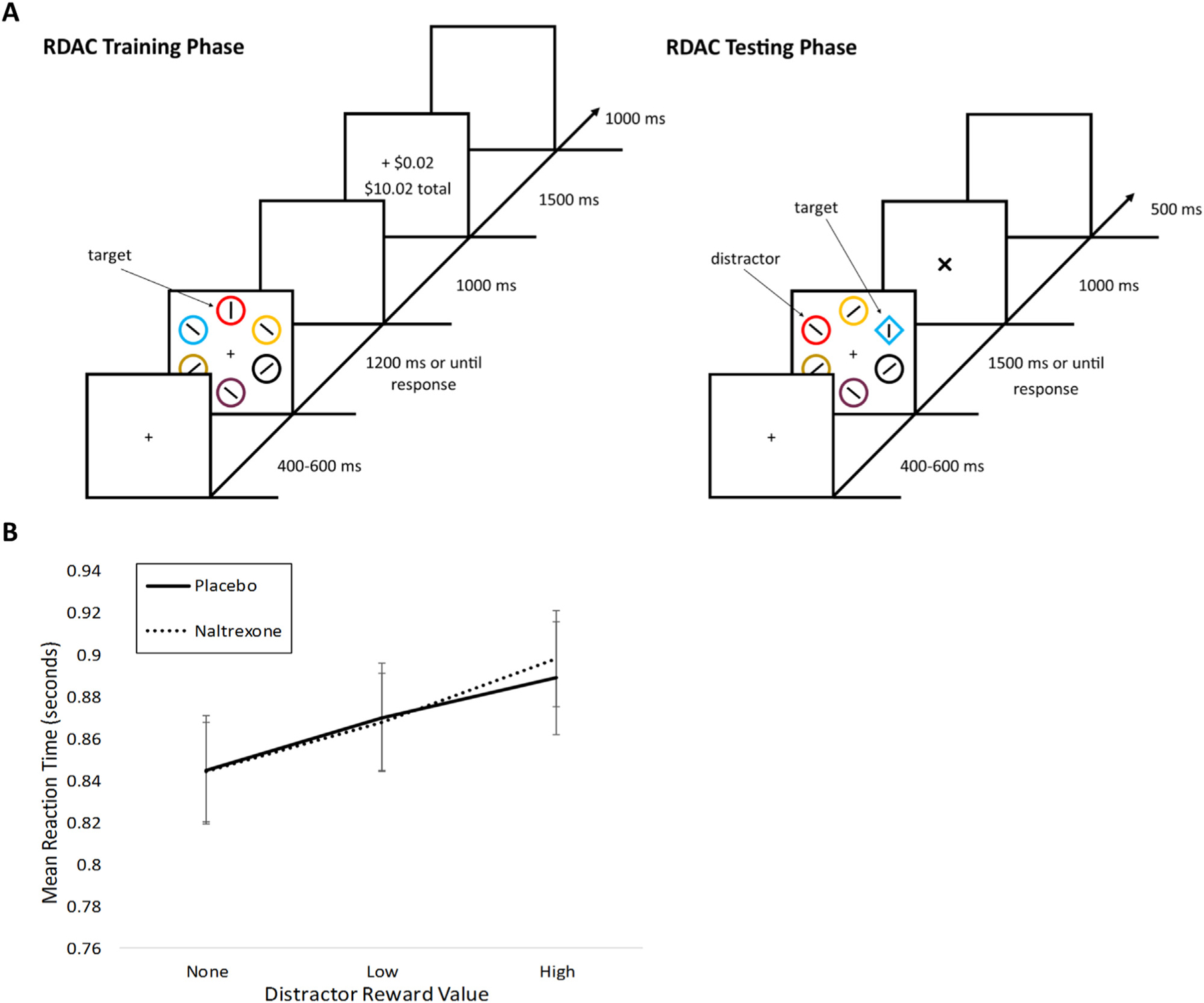
A) In the training phase, participants searched a visual array of colored circles for a target circle colored red or green and indicated by button press the orientation (horizontal or vertical) of a bar within the target circle. Correct responses yielded a probabilistic monetary reward. Incorrect or omitted responses yielded no reward (0¢). The testing phase occurred during fMRI scanning. In this phase, participants were instructed to disregard shape color and search for the odd shape in the presented array, again indicated by button press the bar orientation within the target. No feedback was provided. Half of the trials included non-target red or green shapes, serving as reward-conditioned distractors. B) Mean reaction time (seconds) are shown for testing trials in which no, low, or high reward distractors were present and for placebo versus naltrexone visits. Visit type (placebo versus naltrexone) is indicated by line type.
