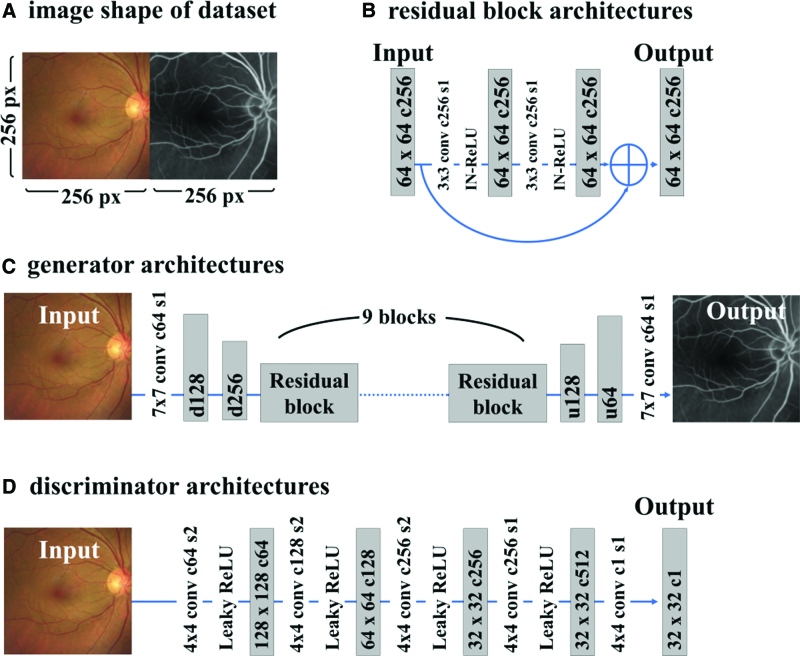
Figure 1.
Schematic of the architecture of CycleEBGAN. (A) The images constituting the dataset were 512 × 256 pixels in size, and fundus photographs and angiographs taken on the same day were arranged horizontally. (B) The residual block repeated the convolutional layer, instance normalization, and ReLU activation twice, and the output was summed with the input. (C) The generator repeated the downsampling twice to reduce the size to 1 quarter of the original size. The residual block was repeated 9 times to translate the image from 1 domain to another. Upsampling was repeated twice to restore the image to its original size. (D) The discriminator repeated the convolution of stride 2 3 times and the convolution of stride 1 twice. Finally, a tensor of 32 × 32 × 1 pixels was generated. c = channel, conv = convolutional layer, CycleEBGAN = energy-based cycle-consistent adversarial networks, d = downsampling layer, IN-ReLU = instance normalization and ReLU activation, px = pixel size, s = stride, u = upsampling layer.