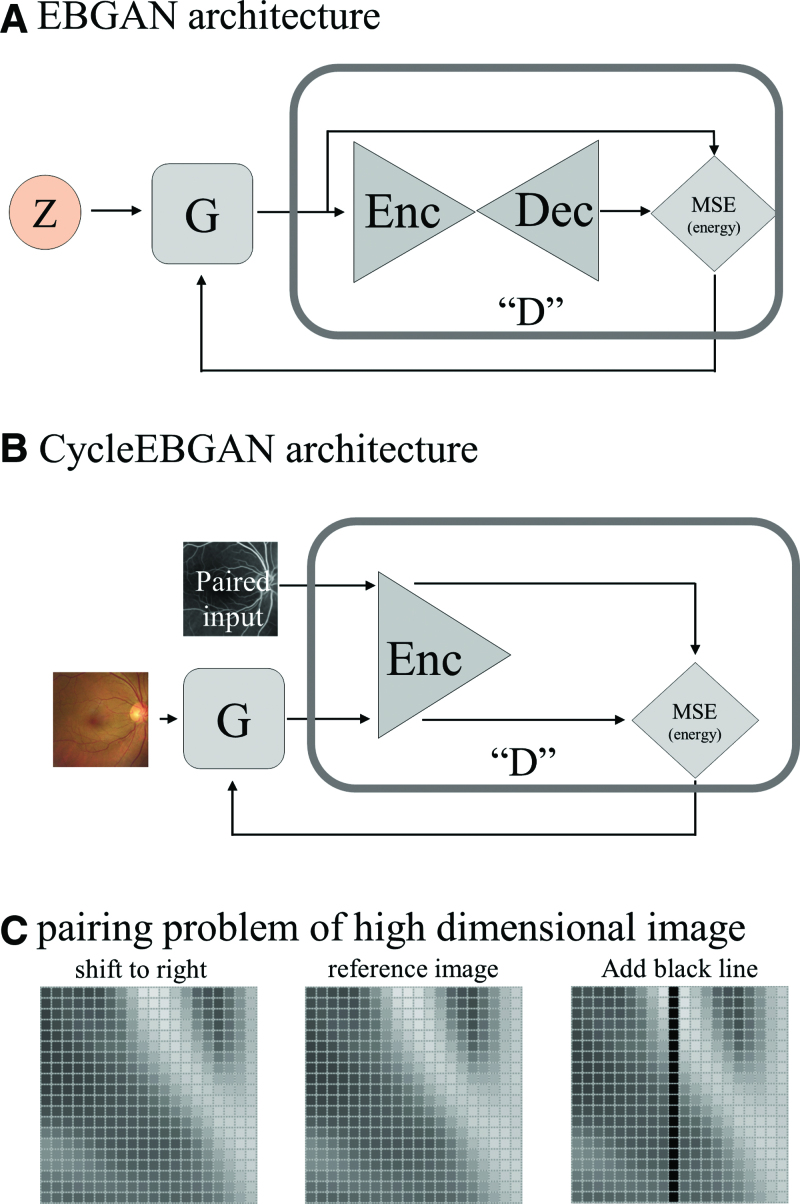
Figure 6.
Comparison of EBGAN and CycleEBGAN. (A) In EBGAN, generator G takes a random vector (z) and synthesizes G(z). The discriminator takes G(z) and transforms it. The discriminator estimates the energy value (E) from the MSE of the G(z) and transformed G(z). (b) In CycleEBGAN, the generator (G) synthesized and simulated an angiograph from a real fundus photograph. The discriminator pairs the simulated angiograph and real angiograph. The discriminator estimates the energy value (E) from the MSE of the 2 images. (c) The central image is a reference image; the left image is the reference image moved to the right by 1 pixel; the right image is the reference image to which a black line has been added. The left and central images look similar. However, the distance (Lp-norm) between them is significantly larger than that between the right and central images. The black line in the right image induces a slight difference. CycleEBGAN = energy-based cycle-consistent adversarial networks, D = discriminator, Dec = decoder, E = energy, EBGAN = energy-based generative adversarial networks, Enc = encoder, G = generator, MSE = mean square error, x = real image, z = latent vector.