Figure 2. Effect of Vitamin D3 or Omega-3s, Compared to Their Matching Placebos, on Risk of DSM-IV Incident MDD at 2 Years by Risk Group of Indicated and Selective Preventiona.
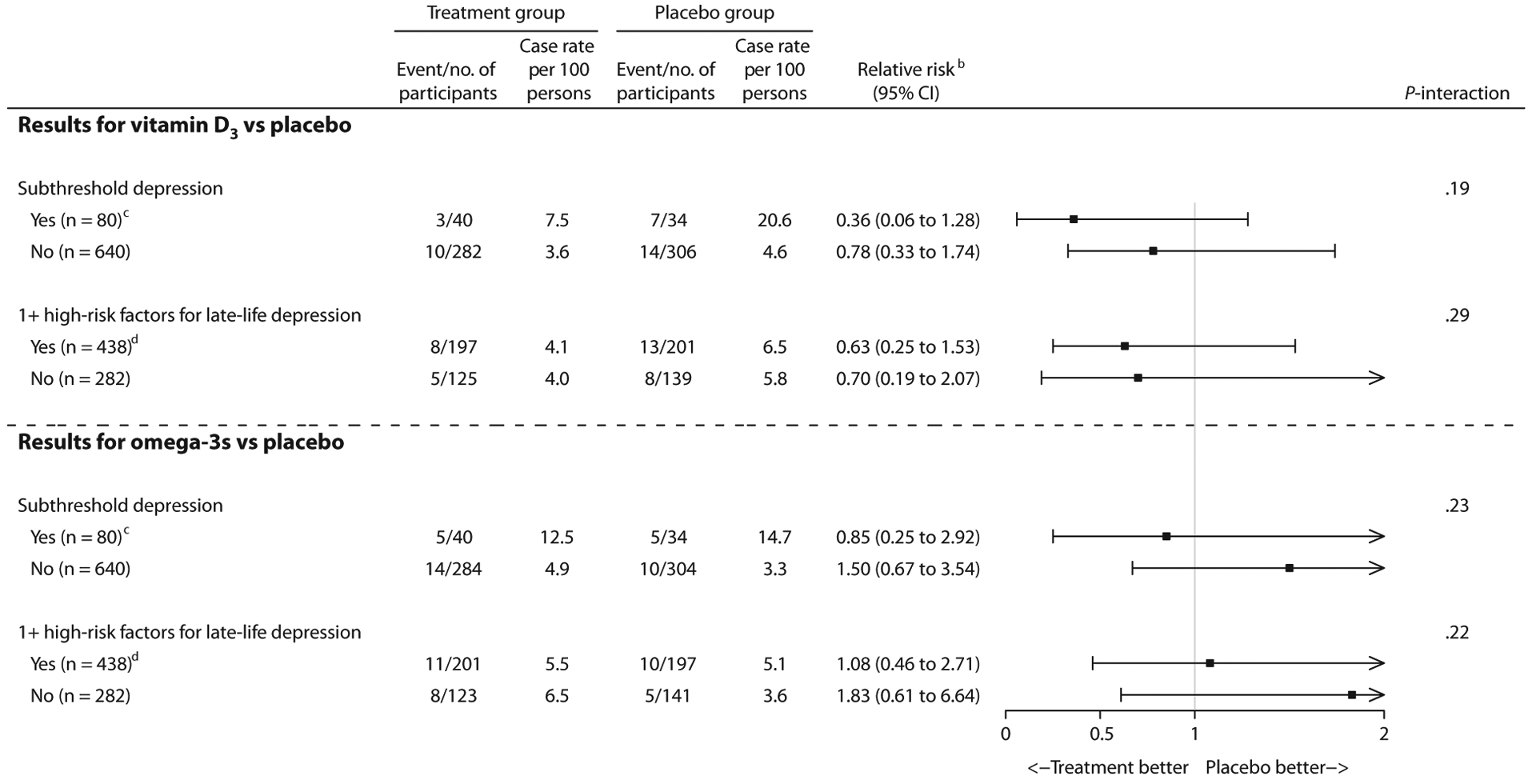
aFrom a total 720 eligible participants, 662 completed follow-up at year 2. For the coprimary outcome of incident MDD, P < .025 was considered as threshold for overall statistical significance.
bRelative risk and its CI were based on exact tests using the exact χ2 score statistic.
cIndicated prevention targeted participants with subthreshold depression, but who did not meet DSM-IV criteria for current major depressive disorders or dysthymia, at baseline.
dSelective prevention targeted participants with ≥ 1 high-risk factor for late-life depression at baseline; see details in Supplementary Appendix 1 (under E. Approach for selective prevention).
eP-interaction was calculated using the Zelen exact test for equal odds ratios. The Zelen exact test was performed to determine whether effects of vitamin D3 or omega-3s, compared to placebo, differ across risk groups of indicated and selective prevention.
