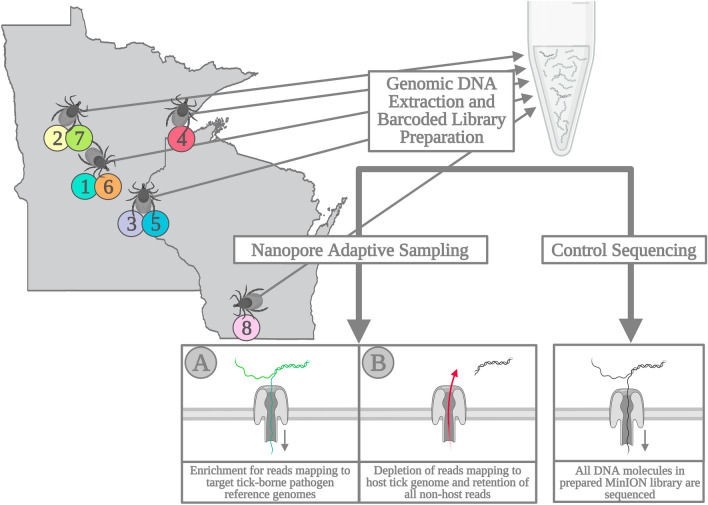
Figure 1.
Comparison of nanopore adaptive sampling (NAS) and control sequencing methods. During NAS, real-time mapping of reads against a user-specified reference allows investigators to target desired genomic regions for sequencing enrichment or depletion. Here, we used select whole genome assemblies to enrich for a select assemblage of tick-borne pathogens (A), resulting in the rejection of unmapped, non-target reads from the sequencing nanopore. Alternatively, we used the genome assembly of the I. scapularis tick vector for a depletion approach in which all mapped host DNA sequences were rejected (B), leading to the retention of any unmapped, non-host reads. A control sequencing experiment was also performed without targeted enrichment or depletion and in which all molecules present in the library were sequenced to completion. Map on the left depicts sampling localities in Minnesota and Wisconsin, USA where tick samples originated. Numbers beneath each locality correspond to tick sample numbers referred to throughout the manuscript. Map created using ArcMap software (v10.8.2, ESRI, Redlands, United States).