Fig. 7.
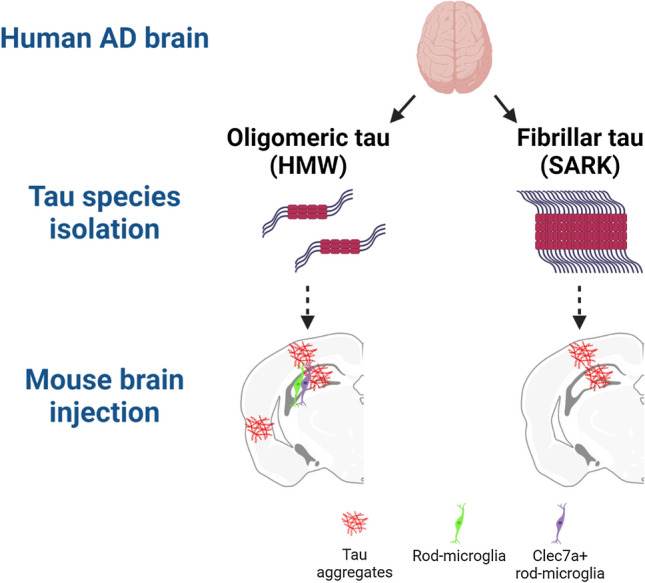
Distinct tau species induce distinct biological effects. Schematic representation of the main findings using BioRender. AD brain-derived tau species were isolated using PBS solubility and SEC (HMW) or sarkosyl insolubility (SARK), obtaining mostly oligomeric forms of tau and mostly fibrillar tau, respectively, after biochemical and EM characterization. Tau samples were then injected into the hippocampus of PS19 and Tau22 tau mouse models. Histological analysis of injected mouse brains revealed extensive neuronal tau pathology (AT8, pS422, AT100 and ThioS positive) in the hippocampus and the overlying cortex in both injection groups, but abundant tau pathology in the peri-/entorhinal cortices as well as Clec7a-positive rod microglia at the injection site only in the HMW tau-injected animals, attributing distinct biological effects to distinct tau species
