Extended Data Fig. 5 |. Reversion of RGI is prevalent across the Variovorax phylogeny.
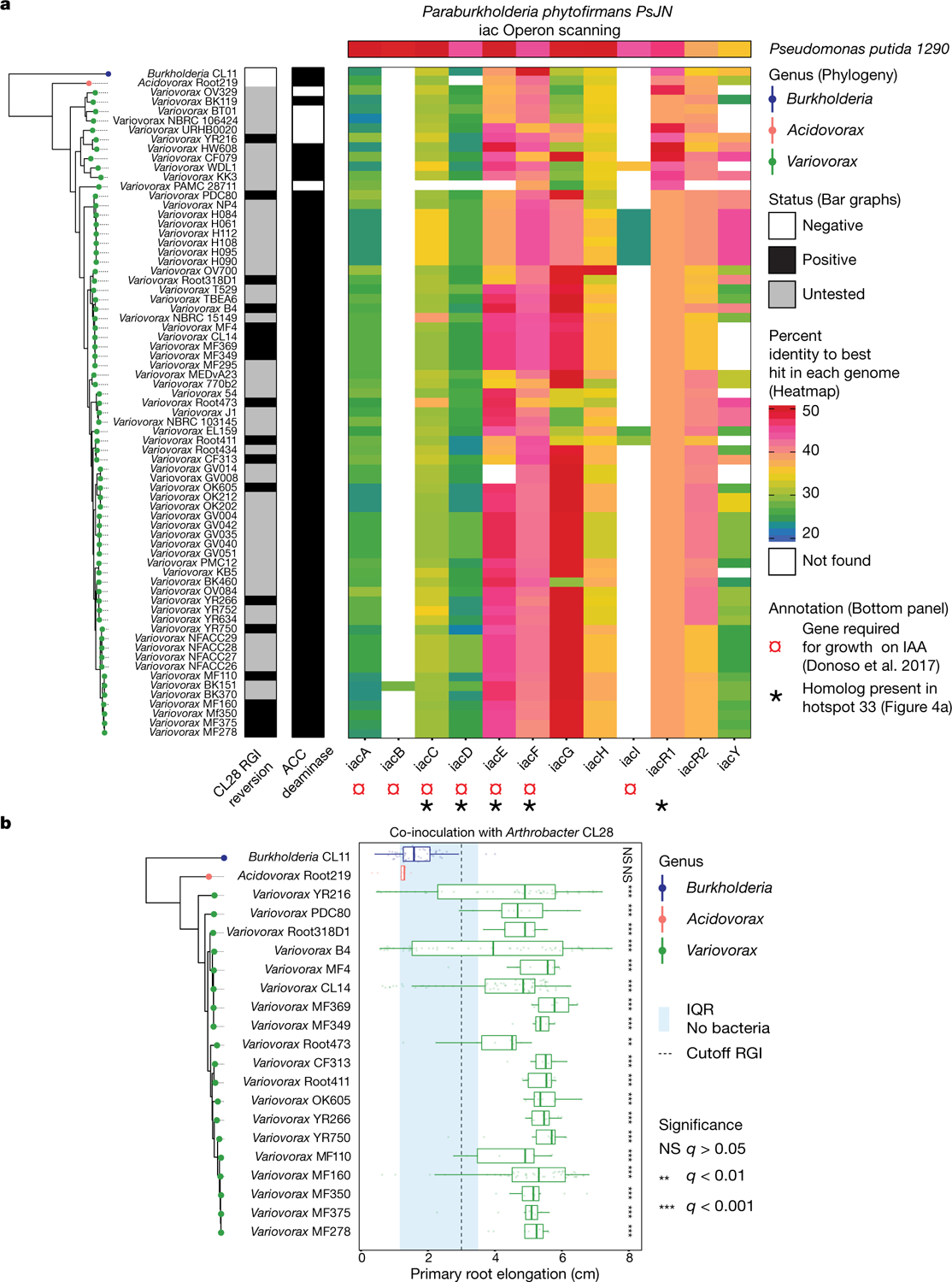
a, Phylogenetic tree of 69 publically available Variovorax genomes and 2 outgroup isolates, Acidovorax root 219 and Burkholderia CL11. The CL28 RGI reversion bar categorizes (positive, negative or untested) the ability of each isolate in the phylogeny to revert the RGI caused by Arthrobacter CL28. The ACC deaminase bar denotes the presence of the KEGG Orthology (KO) term KO1505 (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase) in each of the genomes. The heat map denotes the per cent identity of BLASTp hits in the genomes to the genes from the auxin-degrading iac operon in Paraburkholderia phytophirmans, described by ref.17. Synteny is not necessarily conserved, as these BLAST hits may be spread throughout the genomes. b,All tested Variovorax isolates reverted RGI. Phylogenetic tree of 19 Variovorax genomes and 2 outgroup isolates (Acidovorax root 219 and Burkholderia CL11) that were tested for their ability to revert the RGI imposed by Arthrobacter CL28. The blue vertical stripe denotes the IQR of plants treated solely with Arthrobacter CL28. The dotted vertical line denotes the 3-cm cut-off used to classify a treatment as an RGI. Each box plot is coloured according to the genus classification of each isolate. Significance was determined via ANOVA while controlling for experiment, letters correspond to a Tukey post hoc test. n = 59, 9, 55, 71, 10, 10, 10, 9, 10, 10, 57, 10, 10, 48, 10, 10, 10, 9, 10, 10 and 9 biological replicates across 2 independent experiments.
