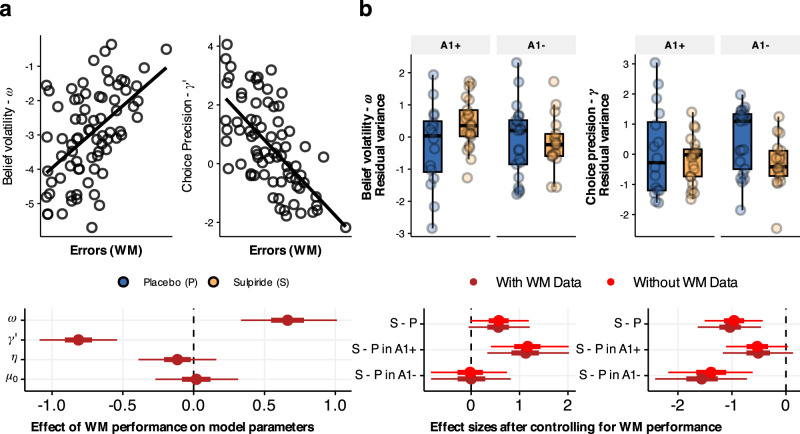
Fig. 6. Working memory performance and computational parameters.
a We reran the parameter estimation with a multilevel model that only included working memory data (number of errors) at the group level effect (and was agnostic about drug and genotype groups). Poorer performance in the spatial working memory task correlated positively with belief volatility and negatively with choice precision and did not affect noise or initial trustworthiness (obtained from sample size n = 75). Effect sizes depicted with means, 50% and 95% CrIs. b Residual variances after accounting for working memory data from the model that is agnostic about drug and genotype data, for parameters and . Boxplots with centre lines as medians, box bounds as 25th and 75th percentiles, and whiskers terminating at maxima/minima (a distance of 1.5 times the IQR away from the 25th and 75th percentiles), with the following samples: in A1+ group, n = 16 placebo, n = 21 sulpiride, and in A1− group n = 21 placebo and n = 17 sulpiride. In the second step, the parameters were estimated with working memory data and drug and genotype variables at the group level. The results of this analysis are shown below as effect sizes with means, 50% and 95% CrIs. The analysis is compared to that with the model that does not include working memory data.