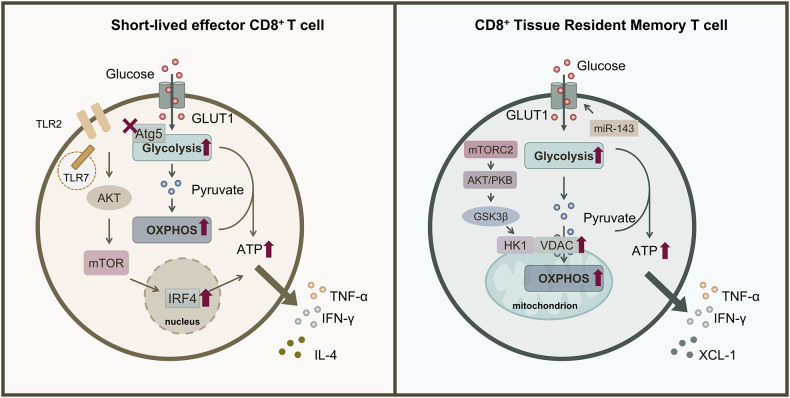
Fig. 3. Effect of altered glycolysis levels on CD8+ T cell effector and memory cell functions.
For short-lived CD8+ T cells, deletion of Atg5 would promote glycolytic activity and OXPHOS, which in turn would lead to energy production. Meanwhile, TLR2 and TLR7 stimulate upregulation of glucose uptake and glycolysis in CD8+ T cells through regulation of the AKT-mTOR pathway and the downstream transcription factor IRF4, thereby promoting effector functions including IL-4, IFN-γ, and TNF-α secretion in CD8+ T cells in vitro. For tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells, during metabolism, mTORC2 promotes respiration by activating PKB or AKT to inhibit GSK3β at the mitochondrial-endoplasmic reticulum (ER) junction, leading to recruitment of HK-I to the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) of mitochondria, thereby promoting metabolite influx into mitochondria to facilitate respiration and thus the rapid production of IFN-γ. Meanwhile, miR-143 targets GLUT1 to promote glucose flux and glycolytic activity, further promoting memory-type functions.