Figure 4. Summary of human duplicated genes implicated in neurodevelopmental functions.
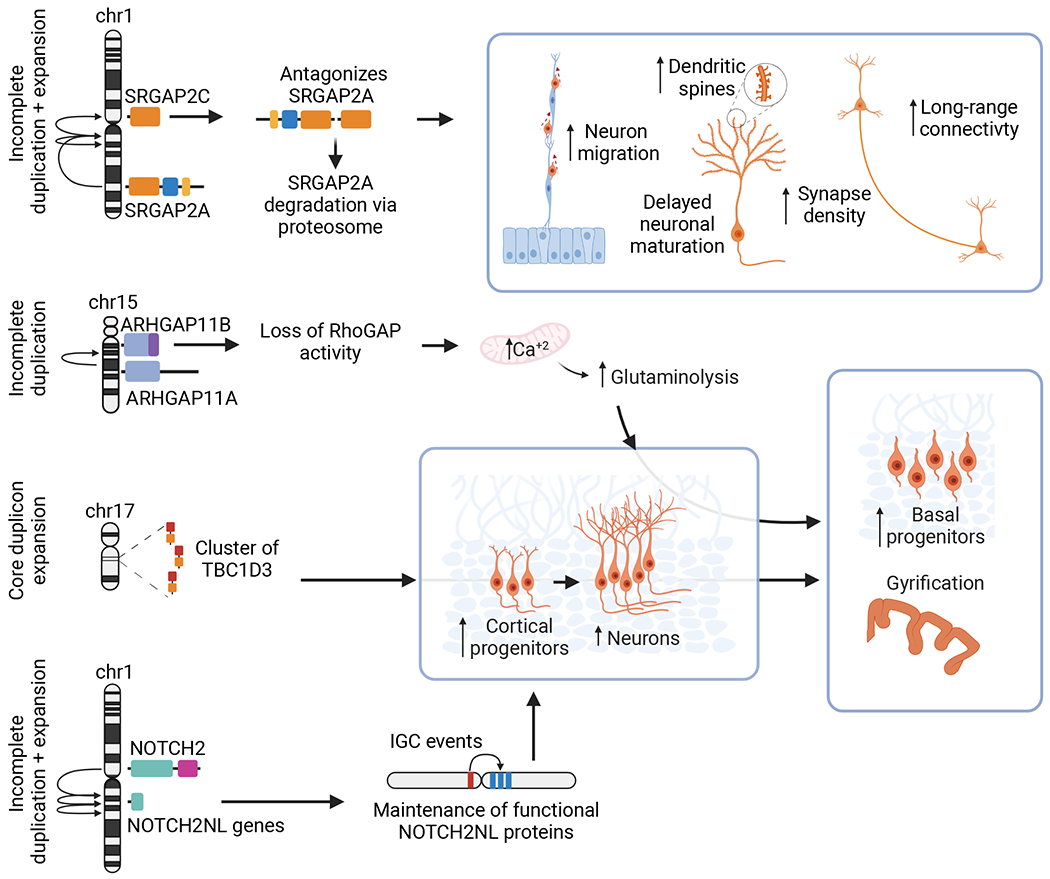
Partially duplicated SRGAP2C antagonizes ancestral SRGAP2A through dimerization of their F-BAR domains, causing its degradation and resulting in increases in the rate of neuronal migration, density of dendritic spines, long-range neuronal connections, and synapse density, as well as delayed neuronal maturation. Truncated ARHGAP11B carries 55 distinct terminal amino acids that result in a loss of its ancestral RhoGAP activity, increasing calcium levels in the mitochondria that result in increased glutaminolysis and a higher abundance of basal progenitors that lead to presence of gyrification. HSE of TBC1D3 located in a core duplicon has been expanded multiple times. Studies have revealed an increase in cortical progenitors and subsequently neurons in the presence of this gene, ultimately resulting in mice with gyrencephalic brains. Incomplete duplication of the N-terminal portion of NOTCH2 and subsequent expansion gave rise to several NOTCH2NL paralogs that remained functional likely due to IGC events and that have been found to directly increase the abundance of cortical progenitors and neurons. Figure created with BioRender.com.
