Figure 1. Mesenchymal stromal cells facilitate venous tip cell fusion during BMP-dependent venous angiogenesis.
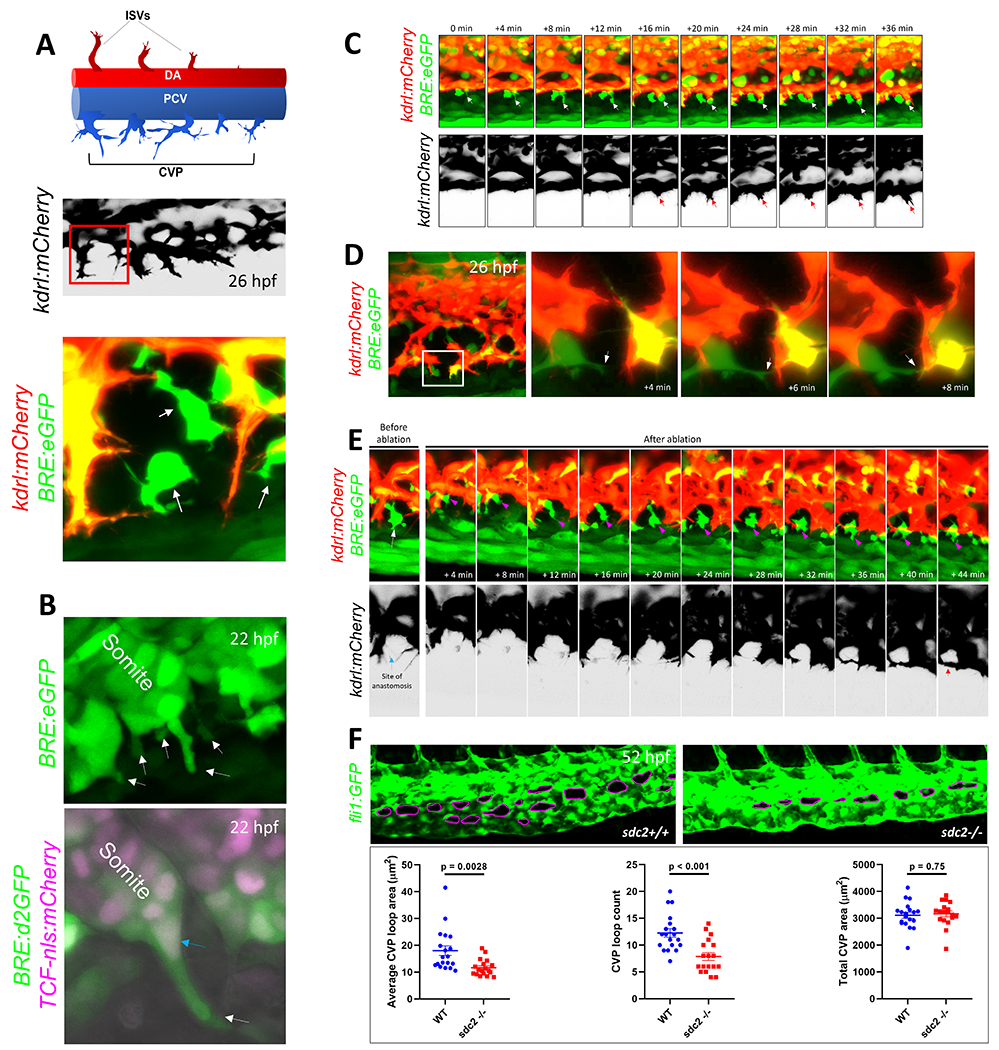
(A) Axial vessels in embryonic zebrafish and the angiogenic sprouts that emanate from them. Top, Schematic depiction of the dorsal artery (DA) and DA-derived intersomitic vessels (ISVs), along with the posterior cardinal vein (PCV) and venous sprouts that make up the caudal vein plexus (CVP). Middle, Maximum projection confocal micrograph of a 26-hour post fertilization (hpf) embryo, showing venous sprouts emerging from the ventral ends of PCV, as revealed by kdrl:mCherry expression. Inverted black/white image. Multiple endothelial sprouts are shown. Lower, Higher magnification of the red boxed region in the middle panel, showing a putative site of anastomosis and multiple filopodial protrusions emerging from endothelial sprouts. Several BMP-responsive (BRE+) mesenchymal-shaped cells are found interposing sites of anastomosis in a Tg(BRE:eGFP);(kdrl:mCherry) double transgenic embryo. (B) Mesenchymal stromal cells (SCs) interpose sites of anastomosis. Top, Still image from a time-lapse maximum projection confocal micrograph of a 22 hpf Tg(BRE:eGFP) embryo, showing a number BRE+ cells emerging from ventral somites. White arrows point to BRE+ cells budding out of ventral somites. Bottom, Maximum projection confocal micrograph of a 22 hpf Tg(BRE:d2GFP);(TCF-nls:mCherry) embryo. High resolution imaging revealed that SC progenitors express d2GFP in the cytoplasm and mCherry in the nuclei. (C) Stills from time-lapse confocal microscopy of ventral PCV at 24 hpf in a Tg(BRE:eGFP);(kdrl:mCherry) embryo, showing the spatio-temporal association of a SCs with an endothelial tip cell during tip cell induction and sprouting. Maximum projection images are shown. White arrow points to SC; red arrow the sprouting tip cell. (D) SCs facilitate anastomosis through cell-cell interaction. Left, Maximum projection confocal image of part of the CVP region at 26 hpf in a Tg(BRE:eGFP);(kdrl:mCherry) embryo, showing several putative sites of anastomosis. Right, Stills from time-lapse confocal microscopy of the white boxed region at higher magnification. The white arrow points to SC filopodial protrusion extending to the adjacent tip cell. Brightness and contrast for the entire image were adjusted using the ImageJ/Fiji software (National Institutes of Health) to reveal filopodial structures. (E) Laser ablation of SCs at sites of anastomosis is ensued by recruitment of new SCs, followed by anastomosis. Stills from time-lapse confocal microscopy analysis of Tg(BRE:eGFP);(kdrl:mCherry) embryo, showing a putative site of anastomosis (blue arrow) prior to laser ablation and a BRE+ SC (white arrow) in the same vicinity. Following irradiation of this SC with 800 nm laser, a new SC gravitates to the same site of anastomosis within minutes, concomitant with completion of anastomosis. The magenta arrow points to the newly emerging SC. Red arrow indicates that a CVP loop is established following anastomosis. (F) Partial loss of SCs in sdc2−/− embryos results in impaired venous angiogenesis. Top, Representative maximum projection confocal micrographs of part of the CVP region in wild-type and homozygous recessive maternal zygotic (MZ) syndecan 2 (sdc2−/−) mutants, expressing the endothelial-specific Tg(fli1:GFP) transgene. The caudal vein plexus loops (CVP loops) in wild-type and sdc2−/− mutants are outlined in magenta. All images are lateral, with anterior to the left. Bottom, Quantification of average CVP loop area, CVP counts and total CVP area at 52 hpf are shown. P-values are shown. An unpaired student’s t-test was used to compare between wild-type fish (N:19 embryos) and sdc2−/− siblings (N:18 embryos).
