Figure 1: A: T1MI and B: T2MI free survival by daily, current cigarette use and age.
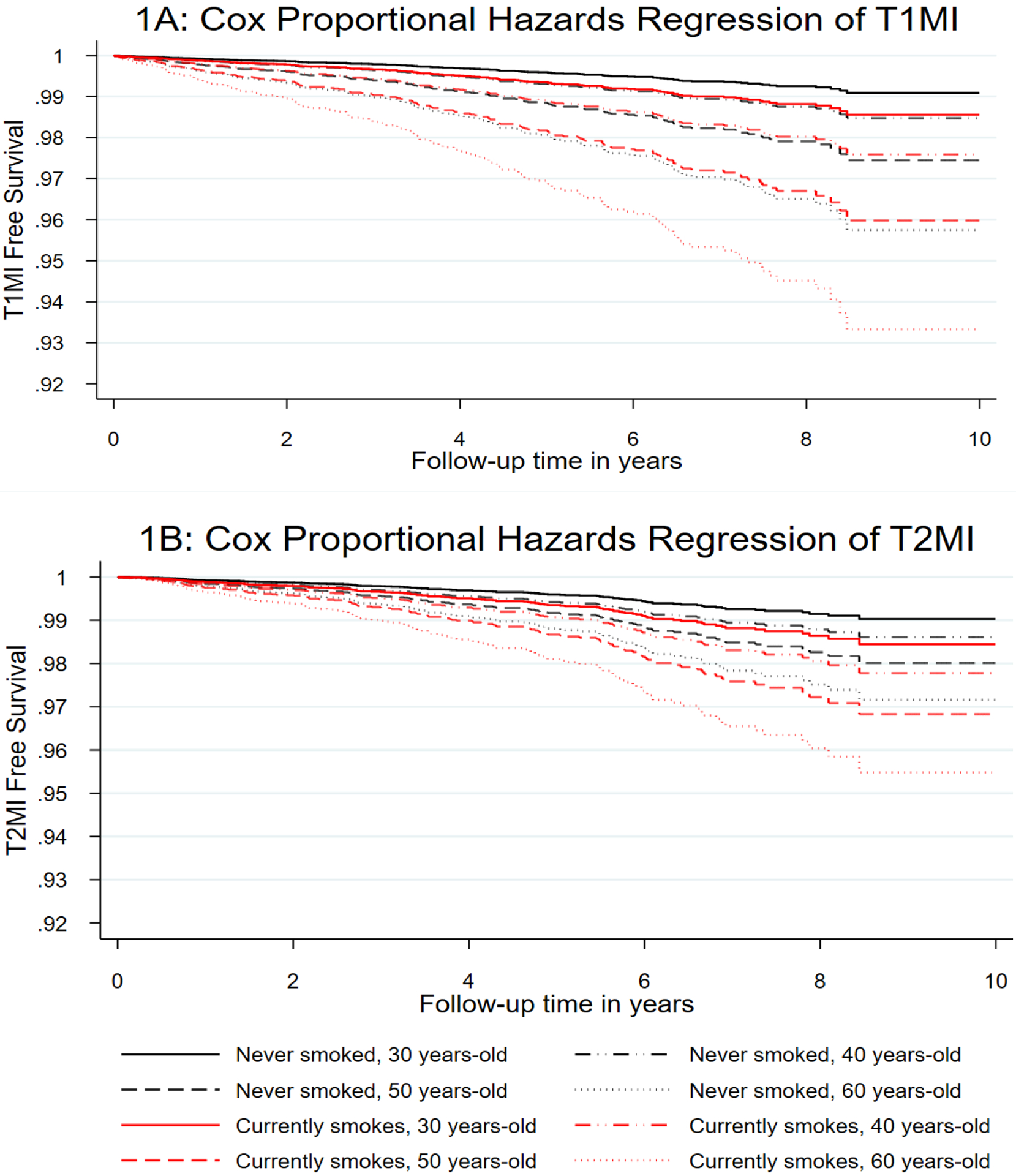
adjusted for number of cigarettes smoked per day for current smokers, sex, race/ethnicity, HCV infection, HBV infection, dyslipidemia, treated hypertension, diabetes, severe chronic kidney disease and time updated viral load and CD4 count. Panel 1A shows that current smokers have a T1MI risk similar to that of a PWH a decade older, whereas the risk of T2MI is similar to that of someone even more than a decade older.
