Figure 5. Antibodies that target intracellular pathogens.
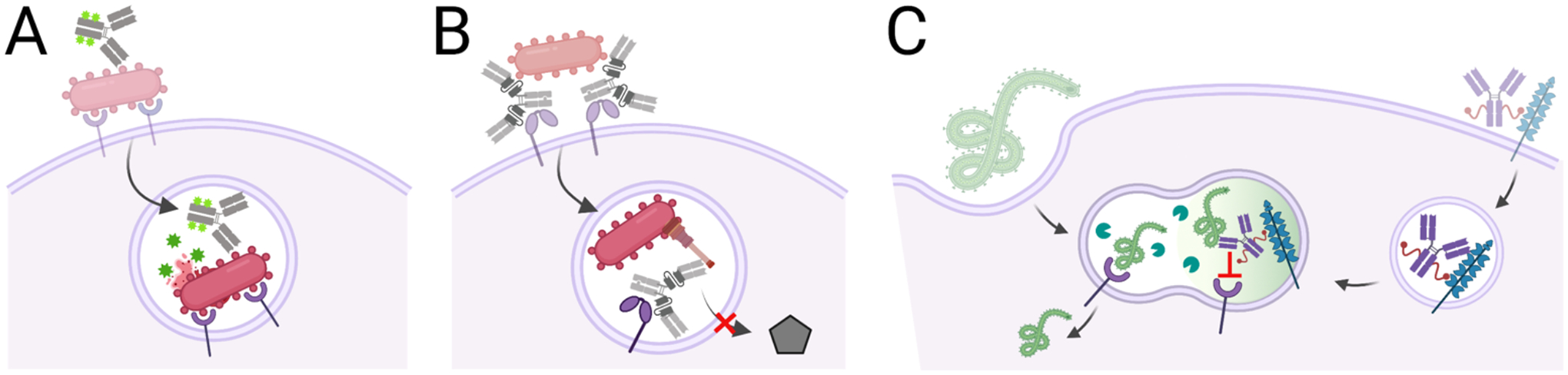
A, Antibody-antibiotic conjugates bind bacterial surface antigens and are internalized with the bacteria by bacterial or immune-mediated mechanisms into endosomal compartments. In this environment, the antibiotic is released to kill co-localized bacteria. B, Bi-specific antibody uses one binding site to bind the Psl antigen on the P. aeruginosa surface and mediate phagocytosis. Once in the endosome, that other antibody binding site blocks Type III secretion to support endosome acidification and bacterial killing. C, Antibodies block Ebola-receptor interactions in the endo-lysosome by hijacking the mannose-6-phosphate receptor to mediate antibody transfer to an endo-lysosome which may already contain Ebola virions. Once co-localized, the antibody blocks glycoprotein-receptor interactions and viral escape into the cytosol.
