Figure 2:
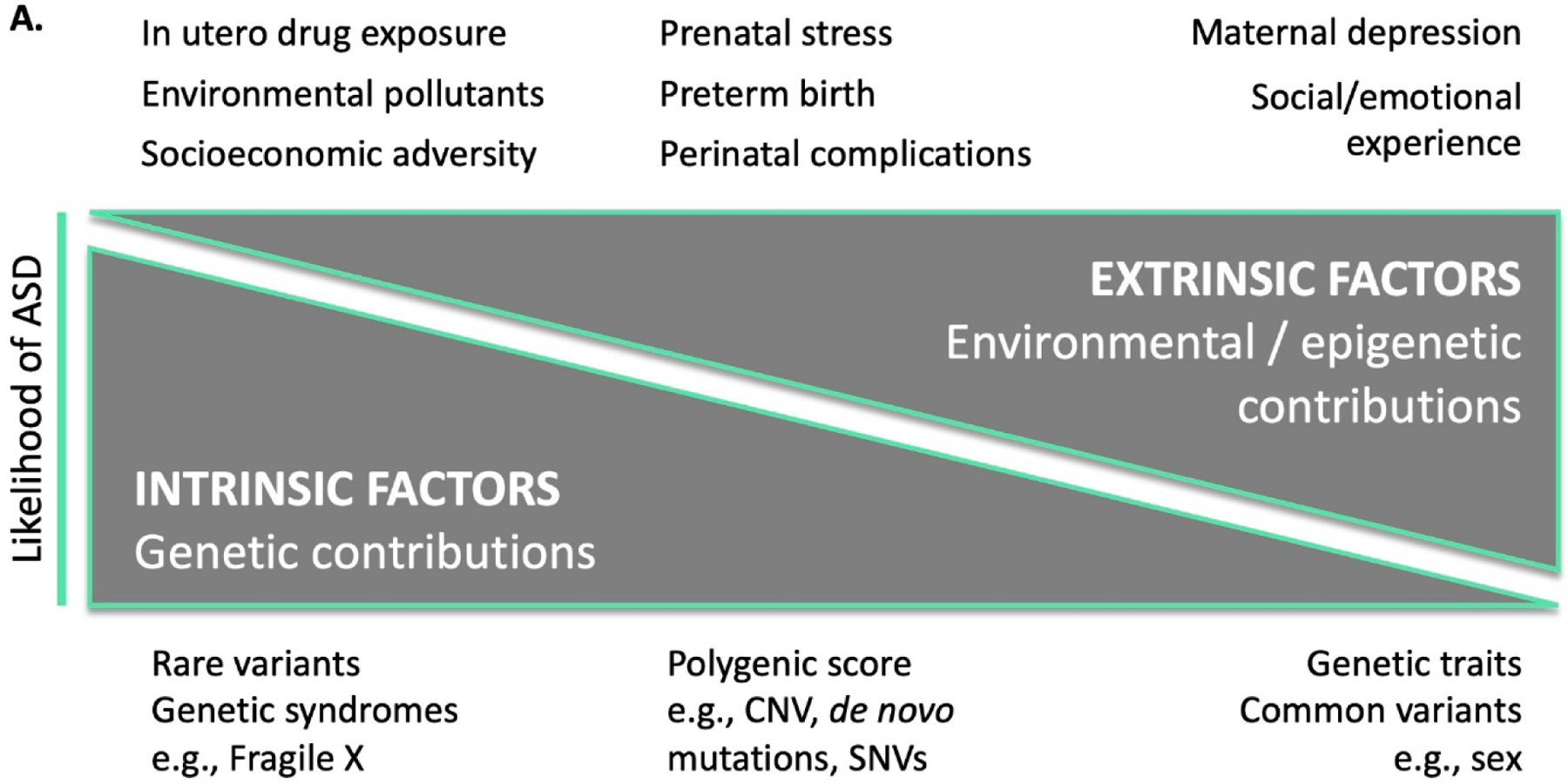
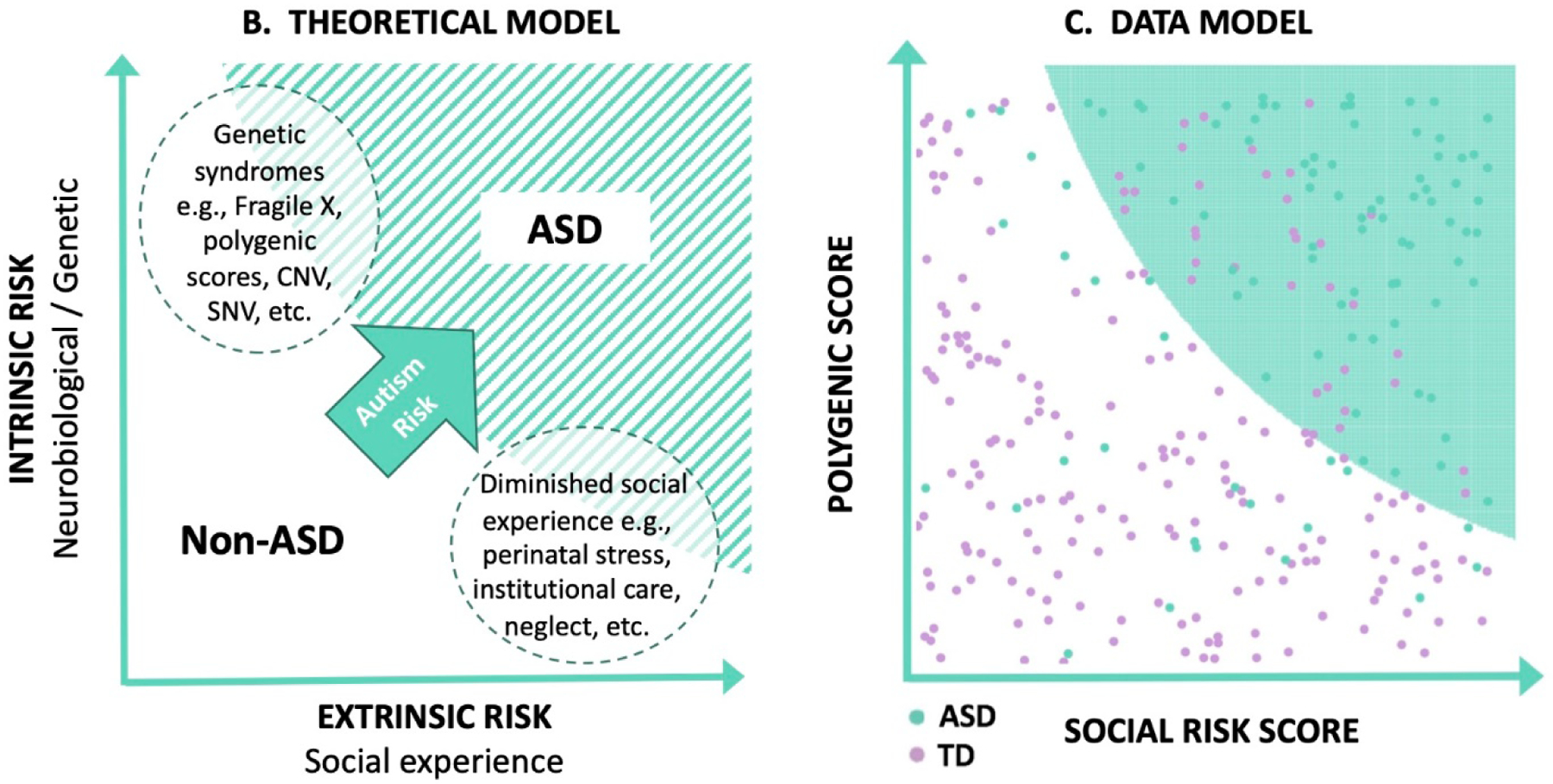
A. Model of intrinsic and extrinsic factors for increasing the likelihood of ASD. B. Theoretical model of how polygenic scores and social risk may predict the development of ASD, with examples given from each axis. C. Simulated model of intrinsic and extrinsic scores for ASD based on multiplicative interaction effects, along with unknown contributions to risk. For illustration purposes, half of the ASD liability derives from the combination of genetic and environmental factors, while unknown causes account for the other half. The shaded green area represents an estimate of the region where children are at high likelihood of ASD, based on an analysis of the simulated data.
CNV, copy number variation; SNV, single nucleotide variant.
