Figure 3. Effect of sex on stroke-induced respiratory dysfunction.
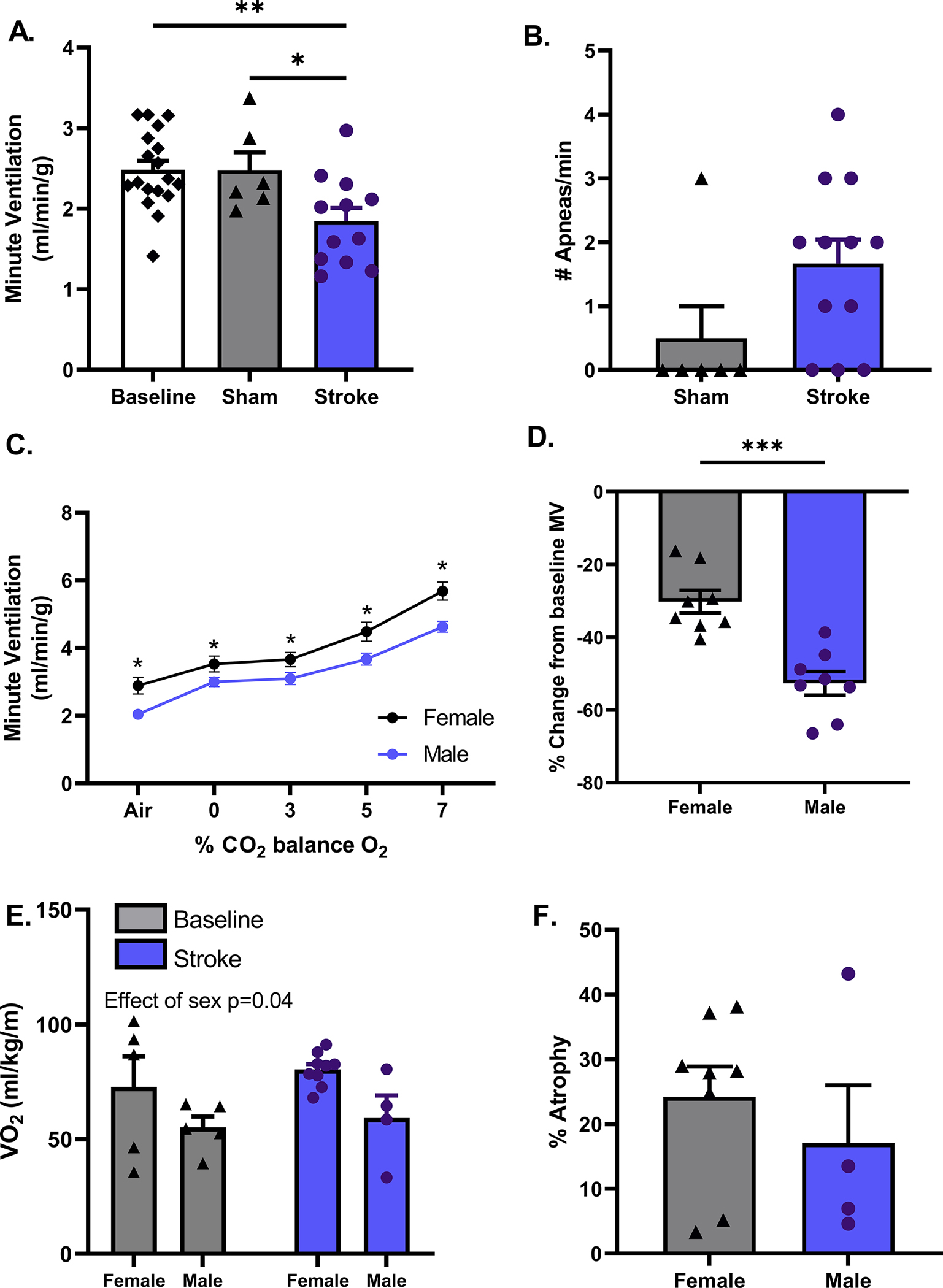
Aged female mice undergoing MCAO display a decrease in MV on day 3 following surgery, compared to baseline & sham p<0.05 (A). Despite having no increase in incidence of apnea, Mann-Whitney test, p=0.07 (B). A, B baseline n=18, stroke n=12, sham n=6. At baseline, aged females display a higher MV under room air conditions and in response to hypercapnia p<0.05, male n=9, female n=12 (C). Aged males displayed a greater percent change in MV from baseline following stroke, males p<0.001, male n=8, female n=8 (D). Metabolic activity was increased in females compared to males at baseline, effect of sex p=0.04, whereas stroke had no effect on metabolic activity in either sex (E). Variations in infarcts did not account for the discrepancies in MV observed between sexes, male atrophy, p=0.44 (F). E-F male n=4–5, female n=5–9
