Figure 5. Evolution of the SIRD phenotype and Progressive cognitive decline correlates with the severity of SIRD in young male mice.
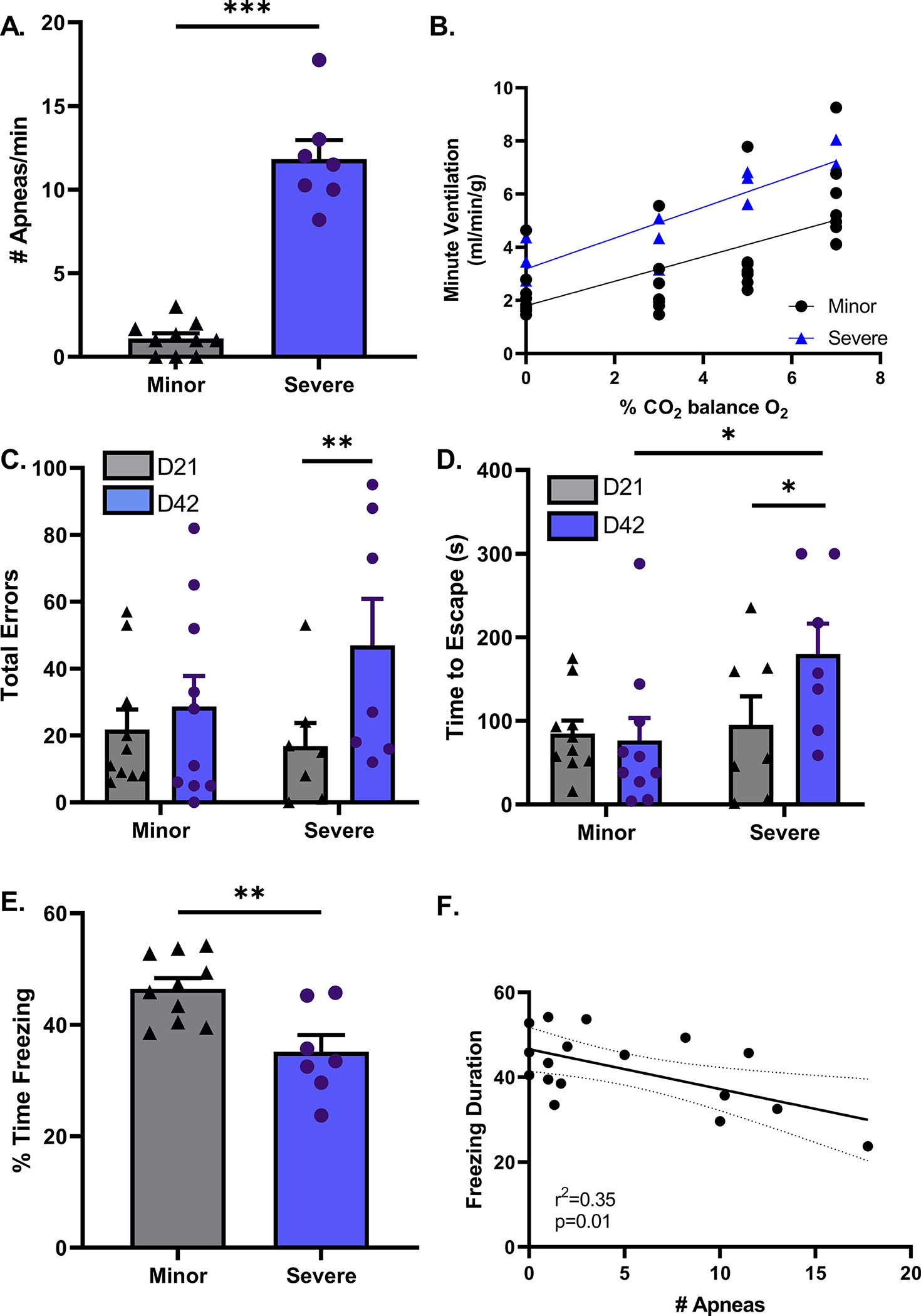
On day 42 post surgery, young stroke mice were stratified into 2 groups based on number of apneas per minute. The minor group experience 5 or less while the severe group had 5 or more apneas a minute (A). Central chemosensitivity did not differ between minor or severe groups, p=0.51 (B). Barnes maze performance was similar on day 21 between minor and severe groups in time to escape and number of errors made. On day 42-post stroke, the minor group is consistent in their performances on day 21. The severe group not only took longer to find the escape hole (p<0.05), but also made more errors than they did on day 21 (p<0.05) (C & D). During contextual fear condition testing, the severe group displays less freezing behavior than the minor group suggesting cognitive impairment, (P<0.01) (E). Linear regression analysis found a negative correlation between the number of apneas and cognitive performance measured as freezing time during contextual fear conditioning test, p=0.01 (F). minor n=10, severe n=7.
