Figure 2.
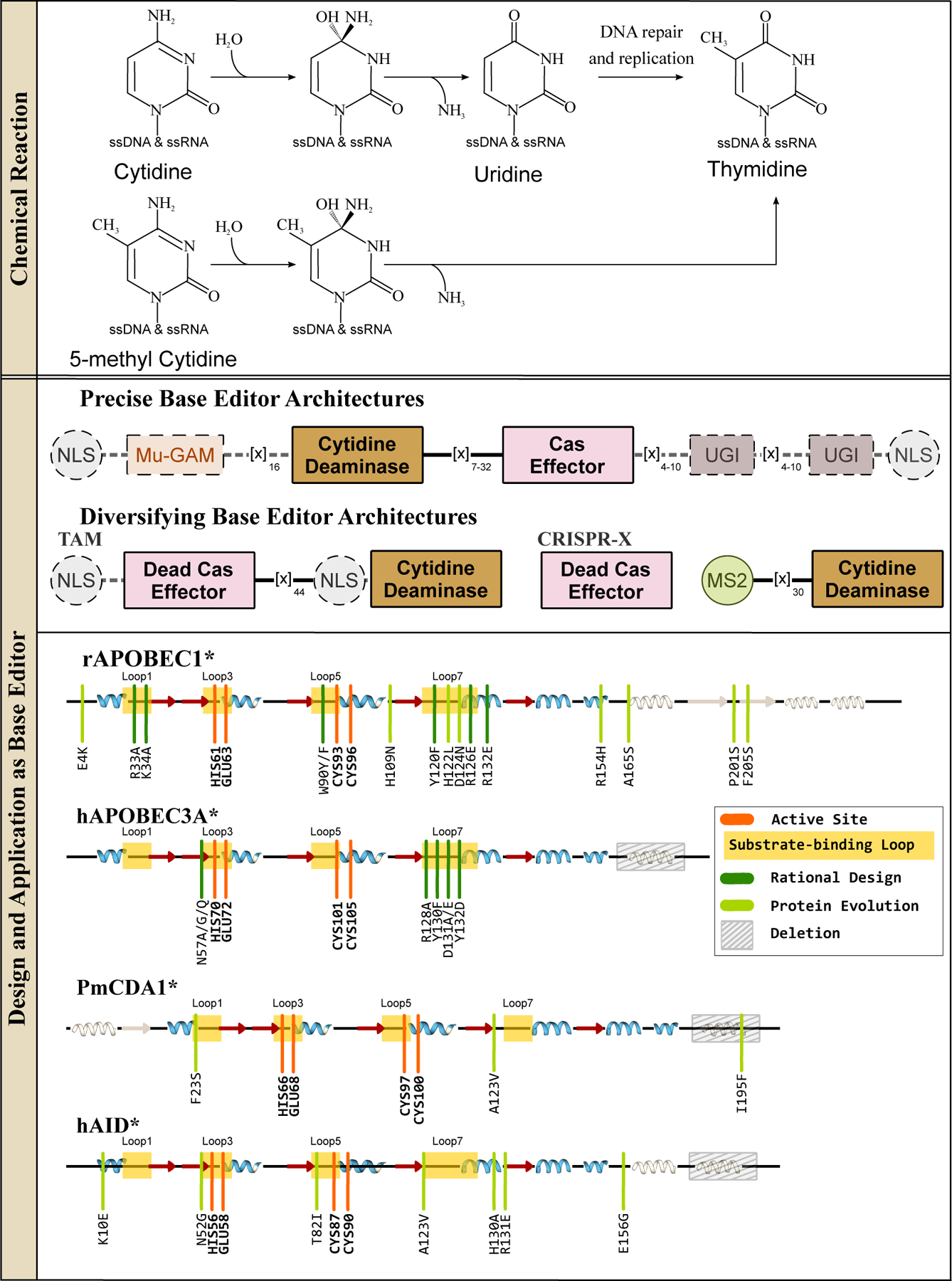
ssDNA cytidine deaminases and their design and applications in genomic DNA base editing. (Top) These enzymes hydrolytically deaminate cytosines or 5-methylcytosines in ssDNA and RNA to yield a uridine or thymine base, respectively. Overall, these reactions give rise to C·G→T·A base pair conversions. (Middle) Representative CBE architectures are shown, with essential and non-essential components indicated with solid and dashed outlines, respectively. (Bottom) Secondary structure alignments of APOBEC and AID deaminases are shown, with an emphasis on the similarity of their core CDA fold. Locations of the substrate-binding loops and active site residues are indicated, and key mutations discovered using either rational design or directed evolution approaches to enhance certain properties of the corresponding CBE are shown in dark and light green, respectively.
