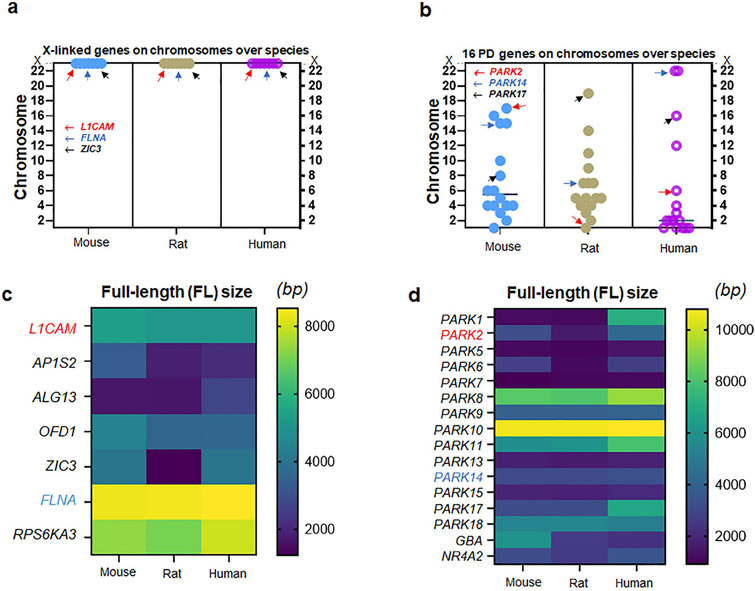
Figure 1. Genes associated with X-linked CH vs. those with fPD.
(a) Locations of seven genes associated with X-linked CH over three species of mice, rats, and humans. Note that all seven genes including L1CAM, FLNA, and ZIC3 are located on the X chromosomes of all three species (b) Locations of sixteen genes associated with familial PD (fPD) over three species of mice, rats, and humans. Note that all sixteen genes including PARK2, PARK14, and PARK17 are located somewhat differently on the autosomes over three species of mice, rats, and humans (c) The full-length (FL) size of seven genes (transcripts) associated with X-linked CH over three species. Note that L1CAM and FLNA show consistent molecular sizes in three species while other genes differ in humans as compared to rodents (d) The FL size of sixteen gene transcripts associated with fPD over three species. Note that PARK2 shows a different length depending on the species, while PARK14 consistent with PARK5, PARK7, PARK9, PARK10, PARK13, and PARK15 demonstrates a consistent FL size over three species.