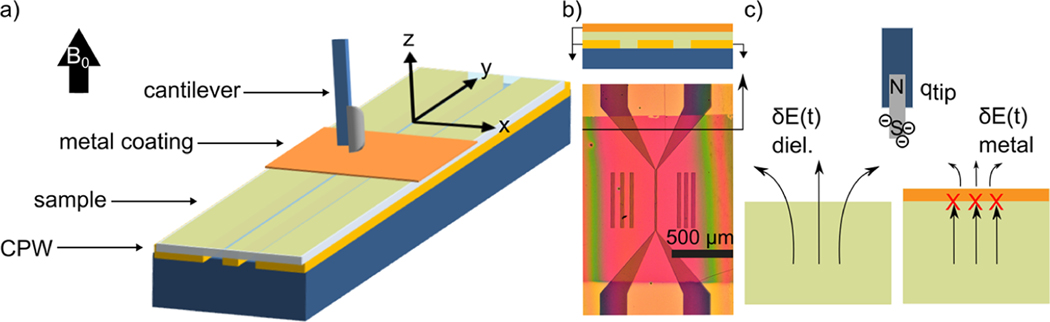
Figure 1.
Magnetic resonance force microscope schematic. A coplanar waveguide (CPW) was produced by depositing 200 nm Cu and 5 nm Au on top of a high-resistivity silicon substrate (). A 200 to 500 nm layer of polystyrene (), doped to 40 mM with 4-amino-TEMPO radicals, was spin-coated on top of the CPW. A 12 nm antistatic layer of gold was then deposited on top via electron beam evaporation. (a) Isometric view showing waveguide, sample, and cantilever. The external field is along the direction, current moves through the waveguide in , and the cantilever oscillates in . (b) Top-down optical image of the waveguide showing dimensions. The CPW center line narrows to a region, where the transverse magnetic field is large enough to invert spins. The metallic antistatic coating is optically transparent and appears red. (c) The antistatic coating blocks stochastic electric fields arising from both thermal fluctuations in the metallic CPW and dielectric fluctuations in the sample.