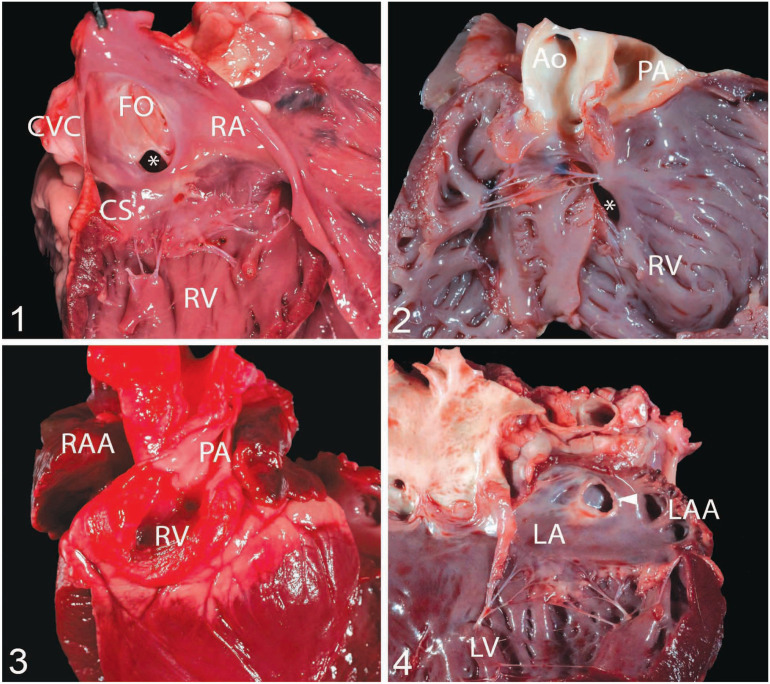
Figures 1–4.
Congenital cardiac malformations identified in our case series from the University of California–Davis, Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital. Figure 1. Atrial septal defect (ASD; asterisk) of the ostium secundum in case 20, a 3-mo-old, castrated male, Boer goat. The 4-mm defect is located above the tricuspid valve but below the fossa ovale (FO; ostium secundum defect). The coronary sinus (CS) is located at 8 o’clock from the defect. Figure 2. Double-outlet right ventricle in case 17, a 7-d-old, female Nubian kid with a ventricular septal defect (asterisk). This goat also had a patent foramen ovale (not shown). Figure 3. Tricuspid atresia in case 23, a neonatal, female, Boer kid that was cyanotic. The right ventricle (RV) sits at the base of the heart and is a closed chamber. The right atrial appendage (RAA = right auricle) is enlarged and congested. This goat also had a 15-mm ASD. Figure 4. Cor triatriatum sinister in case 27, a 2-y-old, male, Boer goat that was euthanized because of urolithiasis. A single defect composed of a membrane (arrowhead) divides the left atrium (LA) into 2 chambers. The left atrial appendage (LAA = left auricle) is not enlarged. Ao = aorta; CVC = caudal vena cava; LV = left ventricle; PA = pulmonary artery; RA = right atrium; RV = right ventricle.