Abstract
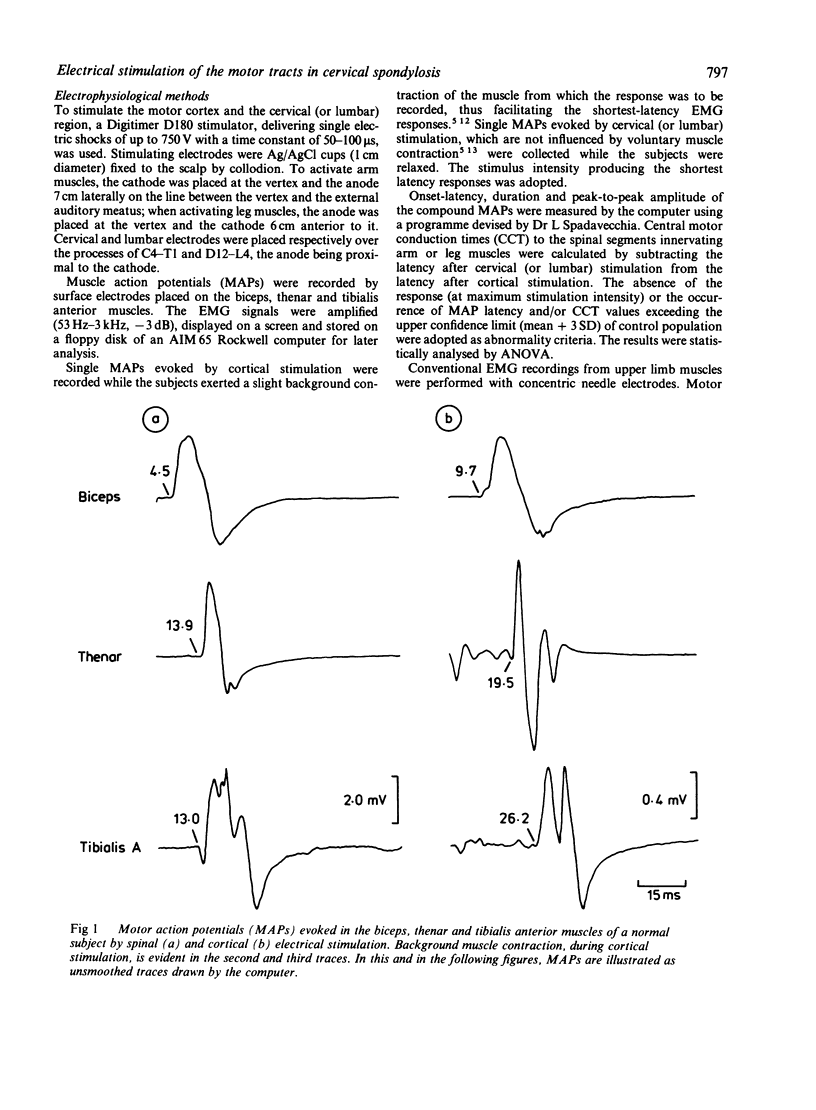
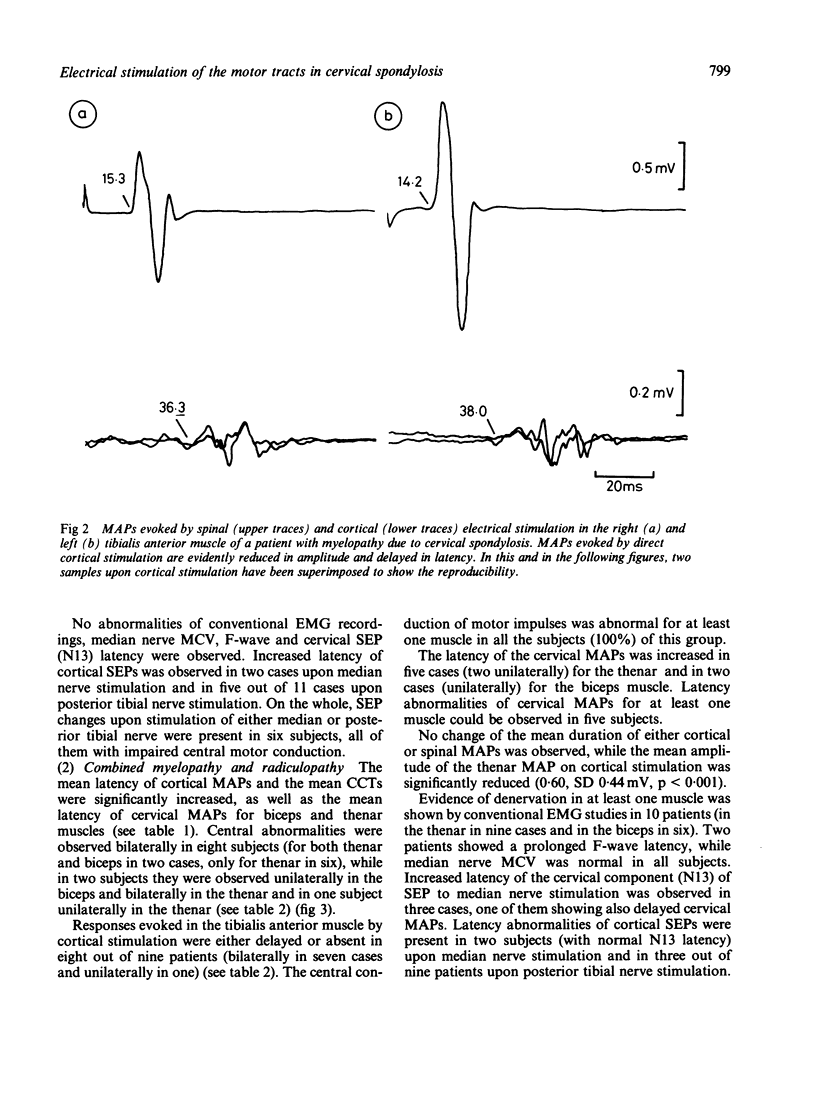
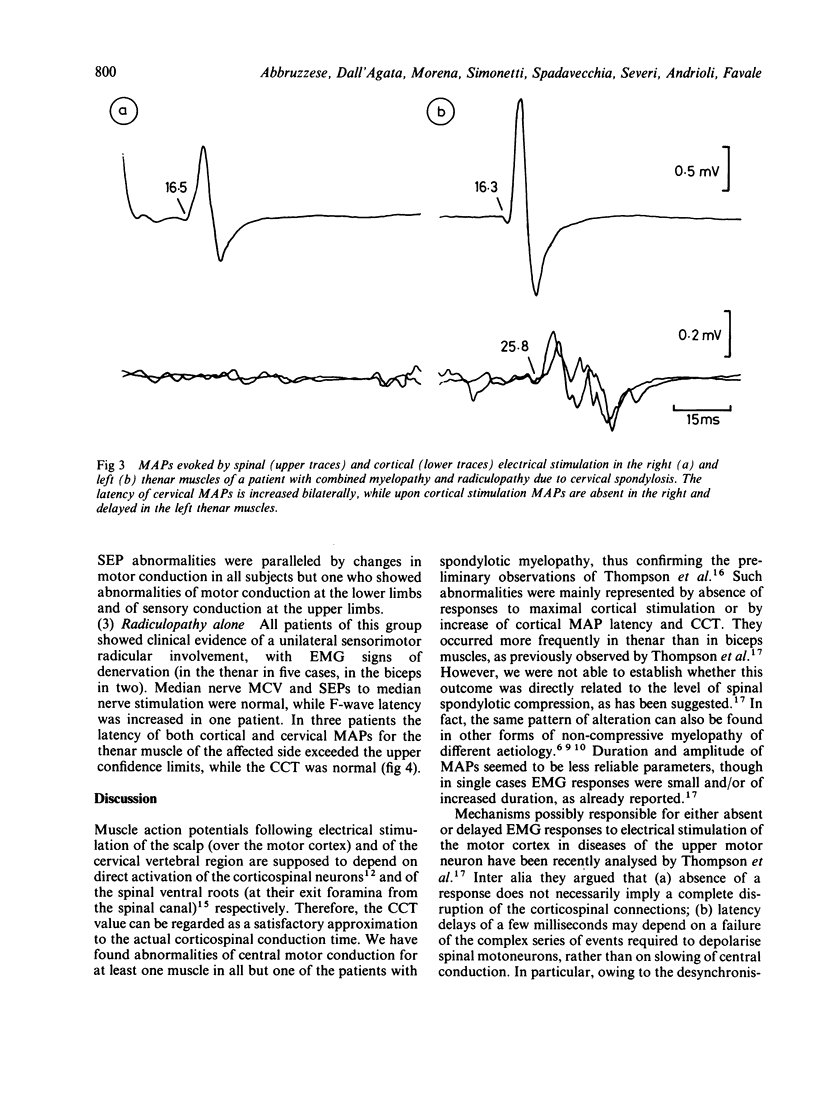
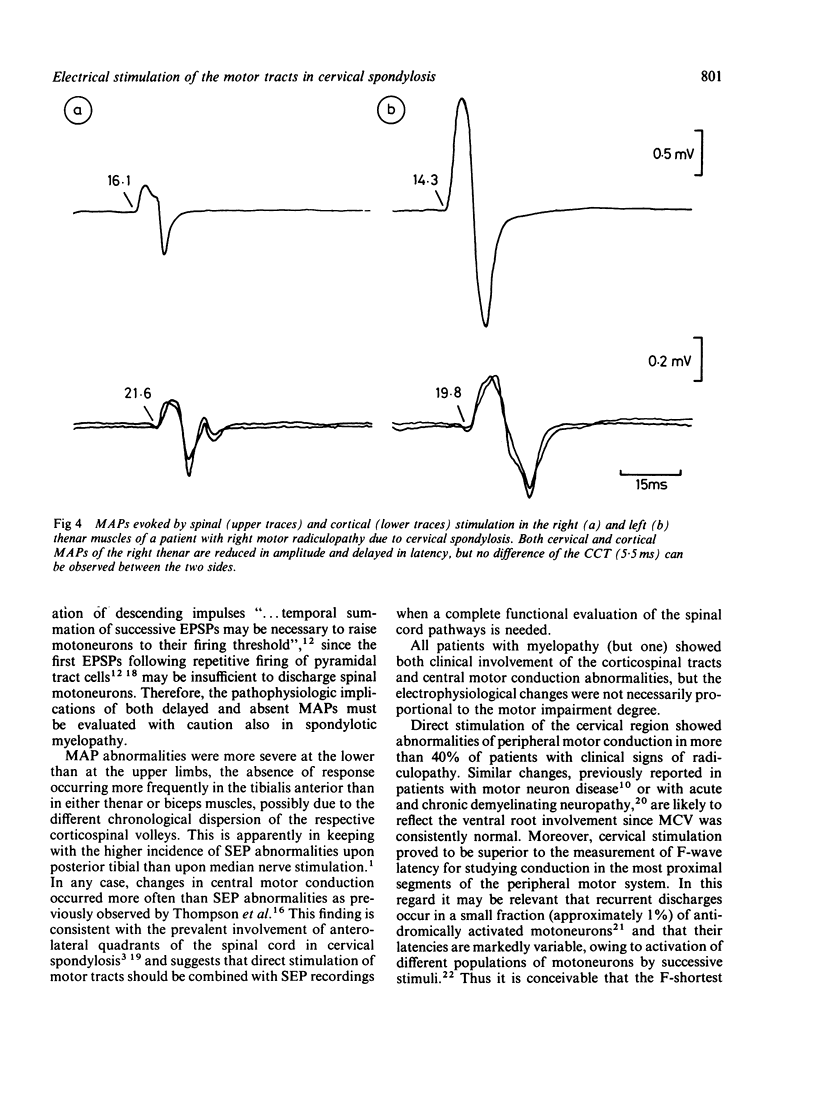
Motor action potentials evoked by percutaneous electrical stimulation of the scalp and of the cervical (or lumbar) vertebral region were recorded from the biceps, thenar and tibialis anterior muscles in 30 patients with cervical spondylosis. Twelve normal controls were matched for age and height. Abnormalities of central motor conduction (absence or increased central delay of cortical responses) for at least one muscle were observed in all (but one) the patients with myelopathy alone or combined with radiculopathy. An increase in latency of the responses evoked by cervical stimulation occurred in 40% of patients with radiculopathy or myelo-radiculopathy. Changes of motor conduction occurred even in the absence of abnormalities of somatosensory evoked potentials, while the opposite was never observed. Direct stimulation of the motor tracts may be of value in the functional assessment of the motor pathways in cervical spondylosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berardelli A., Inghilleri M., Formisano R., Accornero N., Manfredi M. Stimulation of motor tracts in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jun;50(6):732–737. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.6.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berardelli A., Inghilleri M., Manfredi M., Zamponi A., Cecconi V., Dolce G. Cortical and cervical stimulation after hemispheric infarction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jul;50(7):861–865. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.7.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd S. G., Rothwell J. C., Cowan J. M., Webb P. J., Morley T., Asselman P., Marsden C. D. A method of monitoring function in corticospinal pathways during scoliosis surgery with a note on motor conduction velocities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Mar;49(3):251–257. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE E., ROBINSON P. K. Cervical myelopathy: a complication of cervical spondylosis. Brain. 1956 Sep;79(3):483–510. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.3.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. G., Hallett M. Cortical stimulation does not cause short-term changes in the electroencephalogram. Ann Neurol. 1987 May;21(5):512–513. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. M., Rothwell J. C., Dick J. P., Thompson P. D., Day B. L., Marsden C. D. Abnormalities in central motor pathway conduction in multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):304–307. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92683-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Dick J. P., Nakashima K., Marsden C. D. Different sites of action of electrical and magnetic stimulation of the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 20;75(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Odusote K. Amplitude of the F wave: a potential means of documenting spasticity. Neurology. 1979 Sep;29(9 Pt 1):1306–1309. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.9_part_1.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merton P. A., Hill D. K., Morton H. B., Marsden C. D. Scope of a technique for electrical stimulation of human brain, spinal cord, and muscle. Lancet. 1982 Sep 11;2(8298):597–600. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90670-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merton P. A., Morton H. B. Stimulation of the cerebral cortex in the intact human subject. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):227–227. doi: 10.1038/285227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. R., Murray N. M. Corticospinal tract conduction time in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1985 Nov;18(5):601–605. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. R., Murray N. M. Electrical stimulation over the human vertebral column: which neural elements are excited? Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986 Jun;63(6):582–589. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(86)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Day B. L., Rothwell J. C., Dick J. P., Cowan J. M., Asselman P., Griffin G. B., Sheehy M. P., Marsden C. D. The interpretation of electromyographic responses to electrical stimulation of the motor cortex in diseases of the upper motor neurone. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;80(1):91–110. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Dick J. P., Asselman P., Griffin G. B., Day B. L., Rothwell J. C., Sheehy M. P., Marsden C. D. Examination of motor function in lesions of the spinal cord by stimulation of the motor cortex. Ann Neurol. 1987 Apr;21(4):389–396. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Dick J. P., Day B. L., Rothwell J. C., Berardelli A., Kachi T., Marsden C. D. Electrophysiology of the corticomotoneurone pathways in patients with movement disorders. Mov Disord. 1986;1(2):113–117. doi: 10.1002/mds.870010205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willer J. C., Barranquero A., Kahn M. F., Sallière D. Pain in sciatica depresses lower limb nociceptive reflexes to sural nerve stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;50(1):1–5. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. L., Jones S. J. Somatosensory evoked potentials in cervical spondylosis. Correlation of median, ulnar and posterior tibial nerve responses with clinical and radiological findings. Brain. 1985 Jun;108(Pt 2):273–300. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. L., du Boulay G. H., Stevens J. M., Kendall B. E. Computer-assisted myelography in cervical spondylotic myelopathy and radiculopathy. Clinical correlations and pathogenetic mechanisms. Brain. 1986 Apr;109(Pt 2):259–278. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


