Figure 2. Tail vein injection of rAAV induces liver injury, but not hepatic necroptosis, in mice with only hyperglycemia or obesity.
-
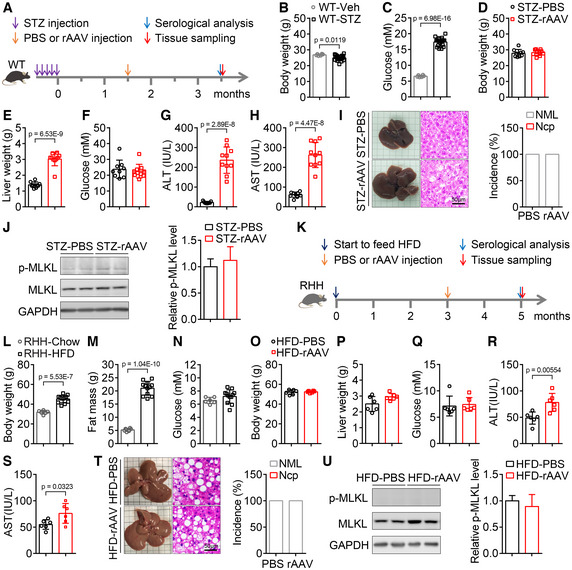
ASchematic of the hyperglycemic mouse model construction by streptozotocin (STZ) and the experimental design for the contribution of hyperglycemia to the liver injury and hepatic necroptosis induced by rAAV injection.
-
B, CBody weight (B) and blood glucose levels (C) were measured 6 weeks later, after injection once a day for 5 consecutive days with vehicle (Veh) or streptozotocin (STZ). n = 6–19 for each group.
-
D–FTwo months after a single injection of rAAV, hyperglycemic mice induced by streptozotocin showed similar body weight (D), blood glucose levels (F) and increased liver weight (E) compared with those mice injected with PBS. n = 9–10.
-
G, HSerum ALT (G) and AST (H) activities of mice in (D).
-
ILiver images, H&E staining of liver sections and the incidence of hepatic necroptosis for mice in (D).
-
JThe hepatic p‐MLKL level of mice in (D).
-
KSchematic of the obese mouse model construction induced by high‐fat diet (HFD) and the experimental design for the contribution of obesity to the liver injury and hepatic necroptosis induced by rAAV injection.
-
L–NBody weight (L), fat mass (M) and blood glucose levels (N) of RHH (Resistance to HFD‐induced Hyperglycemia) mice fed with HFD for 15 weeks. n = 6–12.
-
O–QBody weight (O), liver weight (P) and blood glucose levels (Q) of obese and euglycemic mice in (L) after a single injection of PBS or rAAV for 2 months. n = 6.
-
R, SSerum ALT (R) and AST (S) activities of mice in (O).
-
TLiver images, H&E staining of liver sections and incidence of hepatic necroptosis for mice in (O).
-
UThe hepatic p‐MLKL level of mice in (O).
Data information: In (B–H, J, L–S, U), data are presented as mean ± SD. Student's t‐test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
