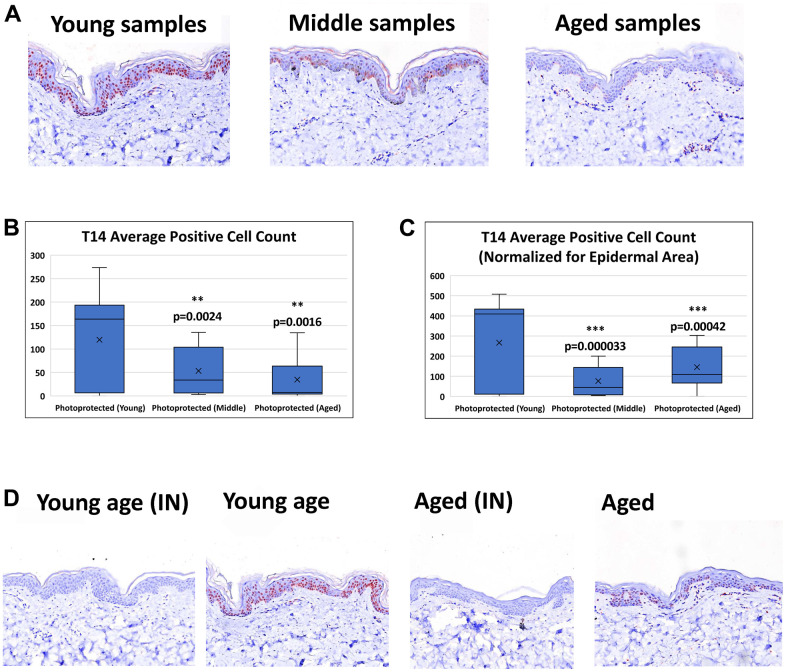
Figure 2.
Detection of T14 in skin. (A) Immunohistochemistry of AChE T14 peptide expression is observed in both the dermis and epidermis. In the epidermis the expression is high in human skin of young subjects (16 to 31 years old), decreases in skin of middle-aged subjects (37 to 45 years old) and further declines in skin of aged subjects (50 to 70 years old). (B) Average number of epidermal cells with a positive AChE T14 peptide antibody stain. Young skin samples have a significantly higher expression (p value of 0.00018) of T14 positive cells compared to its expression in both middle-aged and aged skin samples. (C) Average number of epidermal cells with a positive AChE T14 peptide antibody stain normalized by epidermal area. Young skin samples have a significantly higher expression (p value of 0.0000015) of T14 positive cells per epidermal area compared to its expression in both middle-aged and aged skin samples. (D) Peptide block of T14 and anti-T14 staining of young PP skin sample and aged PP skin sample. Peptide successfully blocked T14 binding of epitope for both young and aged photo-protected skin tissues. N=10 in each group.