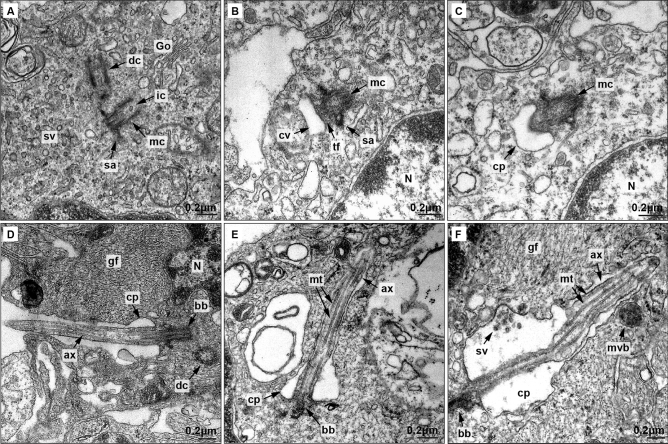
Figure 4.
Electron microscopy analysis of primary cilia biogenesis in low-grade glioma astrocytes.(A–D) Electron microscopy of primary cilia biogenesis. (A) Activated mother centriole (mc) showing subdistal appendages (sa), intracentriolar cargo (ic), and abundant small vesicles (sv) in the distal pole originated in Golgi dictyosomes (Go). The daughter centriole (dc) is also visible. B) Vesicles fuse and form the ciliary vesicle (cv) anchored to mother centriole (mc) by transition fibers (tf). (C) Axoneme starts to grow protruding in the ciliary vesicle (cv). (D) Once the ciliary vesicle binds the cell membrane, cilia axoneme projects to extracellular medium. Ciliary pocket (cp) ang gliofilaments (gf) are also shown. (E) Ultrastructure of primary cilia in low-grade glioma astrocytes. Axoneme is composed by a microtubule cytoskeleton. (F) Extracellular small vesicles and multivesicular body (mvb) are close to the ciliary pocket membrane. Nucleus (N), microtubules (mt), ciliary pocket (cp), basal body (bb), axoneme (ax), gliofilaments (gf) and daughter centriole (dc) are also observed.