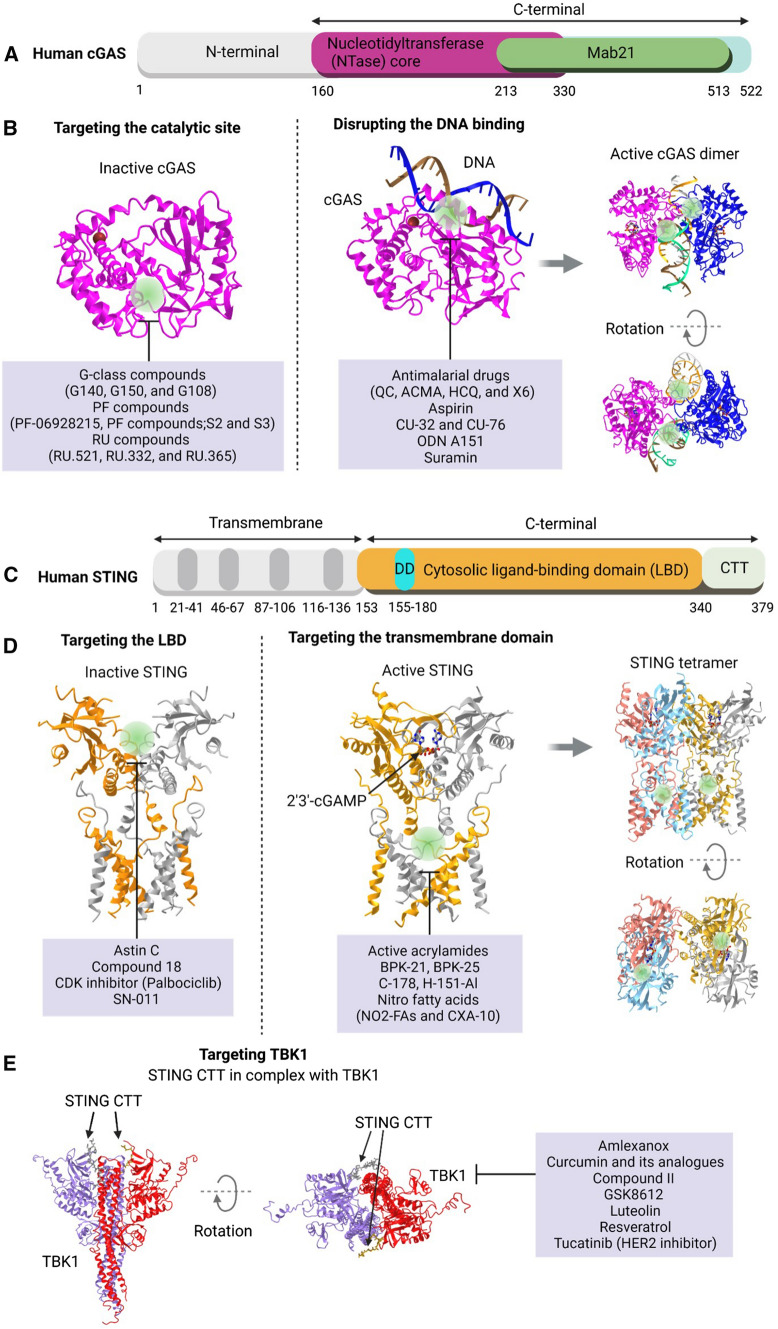
Fig. 2.
Mechanism of inhibitors targeting cGAS, STING and TBK1. A A diagram illustrating the organization of human cGAS domains. B Representative inhibitory targets of human cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS) are shown in three-dimensional structure. Molecules that interfere with the catalytic site and molecules that have been reported to interfere with DNA are each labeled at the target site. The structure shown is modeled as a cGAS catalytic domain (Homo sapiens PDB: 4O68) (Li et al. 2013), cGAS DNA binding domain (H. sapiens PDB: 6CT9) (Zhou et al. 2018), and a dimer (PDB: 4LEZ). C A diagram illustrating the organization of domains in human STING. D Representative inhibitory targets of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) are shown in three-dimensional structure. The molecules targeted at the ligand-binding domain and the transmembrane domain, which are the target sites for inhibition, are indicated. The structure shown was modeled as a ligand-binding domain (H. sapiens PDB: 6NT5), a transmembrane domain (H. sapiens PDB: 6NT7), and a tetramer (G. gallus PDB: 6NT8) (Shang et al. 2019). C The crystal structure of STING CTT in complex with TBK1 (H. sapiens PDB: 6O8C) is shown as a three-dimensional structure, and inhibitors of TBK1 are shown