FIGURE 3.
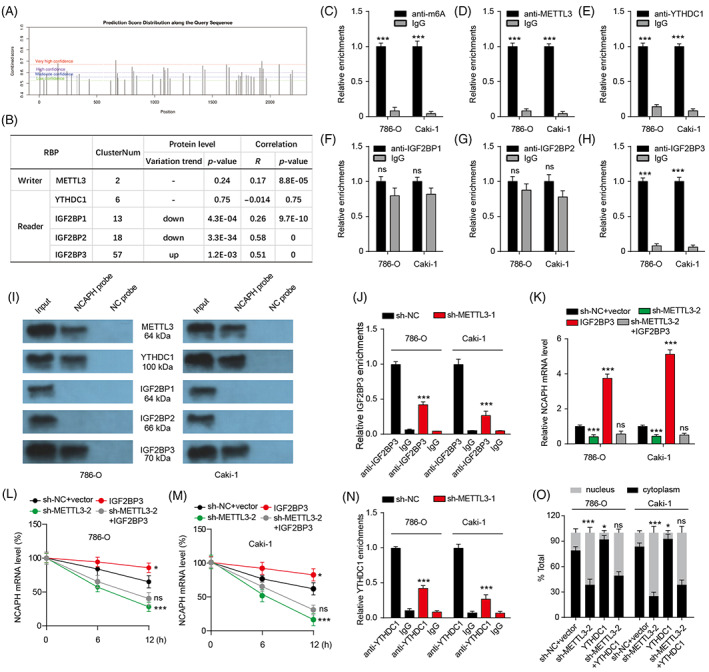
m6A modification of non‐SMC condensin I complex subunit H (NCAPH) mRNA affects its nuclear export and stability. (A) The latent modification sites for m6A in NCAPH mRNA were predicted by SRAMP (sequence‐based RNA adenosine methylation site predictor) database. (B) The table listed the potential binding RBPs which may regulate m6A modification of NCAPH mRNA. (C–H) RIP assays were used to verify the potential interaction between NCAPH mRNA and m6A Writers or Readers. ns p > 0.05; ***p < 0.001 versus IgG. (I) Pull‐down assays were used to verify the potential interaction between NCAPH mRNA and m6A Writers or Readers. (J) RIP assays show the effect of METTL3 depletion on the binding between NCAPH mRNA and IGF2BP3. ***p < 0.001 versus sh‐NC. (K) NCAPH expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) cells with METTL3 depletion or IGF2BP3 overexpression. ***p < 0.001 versus sh‐NC + vector; ns p > 0.05 versus sh‐METTL3‐2. (L and M) Time‐course qRT‐PCR analyses of the relative abundance of NCAPH in ccRCC cells with METTL3 depletion or IGF2BP3 overexpression treated with actinomycin D (10 μg/ml). *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 versus sh‐NC + vector; ns p > 0.05 versus sh‐METTL3‐2. (N) RIP assays show the effect of METTL3 depletion on the binding between NCAPH mRNA and YTHDC1. ***p < 0.001 versus sh‐NC. (O) The distribution of NCAPH mRNA in nucleus and cytoplasm in ccRCC cells with METTL3 depletion or YTHDC1 overexpression. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001 versus sh‐NC + vector; ns p > 0.05 versus sh‐METTL3‐2. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
