Figure 2. Transgene construct and GCaMP6s expression.
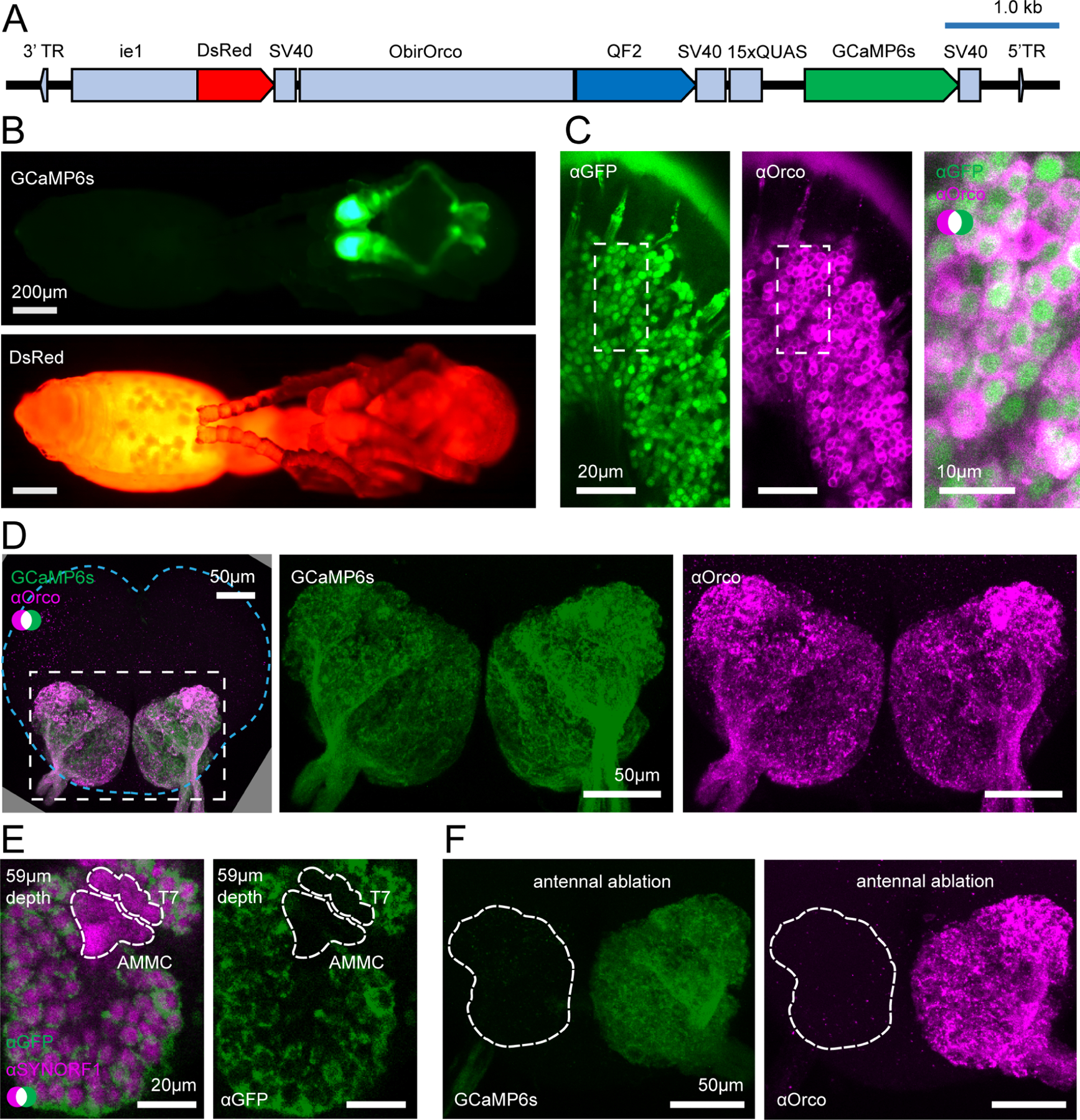
(A) Construct design. (B) Transgenic pupa under epifluorescence: GCaMP6s (top); DsRed (bottom); see Fig. S1 for comparisons with wild types. (C) Anti-GFP (green, cytoplasmic) and anti-Orco (magenta, membrane bound) densely label OSNs in the antennal club (max z-projection through 3 1μm slices). (D) GCaMP6s and anti-Orco signal co-localize in the ALs (max z-projection through the AL); brain contour is shown with cyan line. (E) Anti-SYNORF1 (magenta; neuropil) and anti-GFP (green) staining from a single optical slice in the AL. T7: T7 cluster of glomeruli; AMMC: antennal mechanosensory and motor center. (F) Unilateral ablation of the antenna eliminates GCaMP6s (green, left) and anti-Orco signal (magenta, right) from the AL (max z-projections; white outline indicates the AL boundary as determined from phalloidin stain). See Figs. S1–S2 for additional characterization of GCaMP6s ant brains. See Fig. S3 for genomic analyses of GCaMP6s ants.
