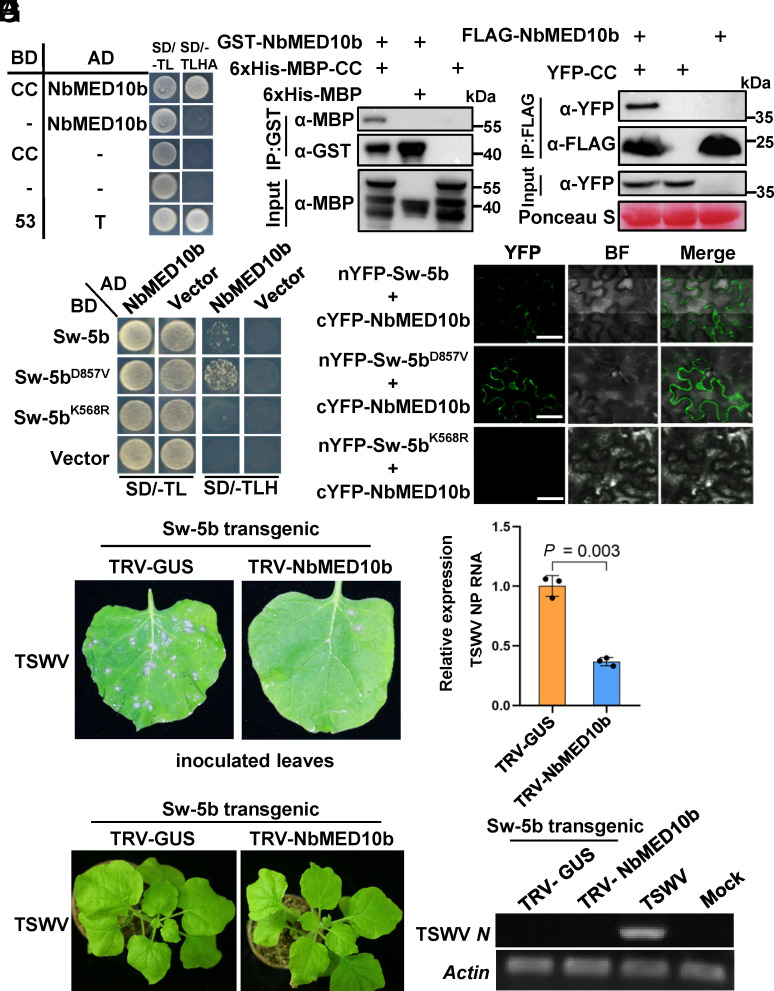
Fig. 1.
Sw-5b CC domain interacts with NbMED10b, a negative regulator of the Sw-5b-mediated defense against TSWV infection. (A) A yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assay result showing an interaction between NbMED10b and Sw-5b CC domain. The transformed yeast cultures were grown on the solid SD dropout medium lacking Trp and Leu (SD/-TL) and the dropout medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (SD/-TLHA), respectively. (B) A GST pull-down assay result showing the interaction between the GST-NbMED10b and 6×His-MBP–Sw-5b-CC. 6×His-MBP–Sw-5b-CC, 6×His-MBP, and GST-NbMED10b were expressed individually in Escherichia coli and then purified. The purified 6×His-MBP–Sw-5b-CC or 6×His-MBP was incubated with GST-NbMED10b followed by the pull-down assay using glutathione-sepharose beads. The blots were probed with an anti-GST- or anti-MBP-specific antibody. (C) A coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay for the interaction between NbMED10b and the Sw-5b CC domain. FLAG-NbMED10b was coimmunoprecipitated with YFP-CC from N. benthamiana leaf extracts. The blots were then probed using an anti-FLAG or an anti-YFP antibody. (D) A Y2H assay result showing the interaction between NbMED10b and Sw-5b, Sw-5bD857V, or Sw-5bK568R mutant. The transformed yeast cultures were grown on the SD/-TL and the SD/-TLH dropout plates, respectively. (E) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay results showing the interaction between NbMED10b and Sw-5b, Sw-5bD857V, or Sw-5bK568R mutant. The nYFP- or cYFP-tagged proteins were transiently coexpressed in N. benthamiana leaf cells and then imaged under confocal microscopy. The YFP signal is shown in green (Scale bars, 20 μm.). (F) The NbMED10b-silenced or nonsilenced Sw-5b transgenic N. benthamiana plant leaves were inoculated with TSWV-infected crude leaf extracts. The TSWV-inoculated leaves were photographed at 3 d post TSWV inoculation (dpi) to show the number of HR loci. (G) The accumulation level of TSWV RNA in the inoculated leaves shown in (F) was determined through qRT-PCR using TSWV N gene–specific primers. All the inoculated leaves were harvested at 3 dpi. The expression levels of NbActin in these assayed leaf samples were used as the internal control. Data are presented as the means ± SE (three biological samples per treatment). (H) Phenotype of systemic leaves of the NbMED10b-silenced and nonsilenced Sw-5b transgenic N. benthamiana plants inoculated with TSWV. The plants were photographed at 14 dpi. (I) RT-PCR detection of TSWV RNA in the systemic leaves of the plants shown in the panel (H) at 14 dpi using TSWV N gene–specific primers. The crude extract from a TSWV-infected N. benthamiana leaf sample was used as the positive control. The leaf sample from a mock-inoculated Sw-5b transgenic N. benthamiana plant was used as the negative control. The expression levels of NbActin in the assayed samples were used as the internal controls.