Fig. 2.
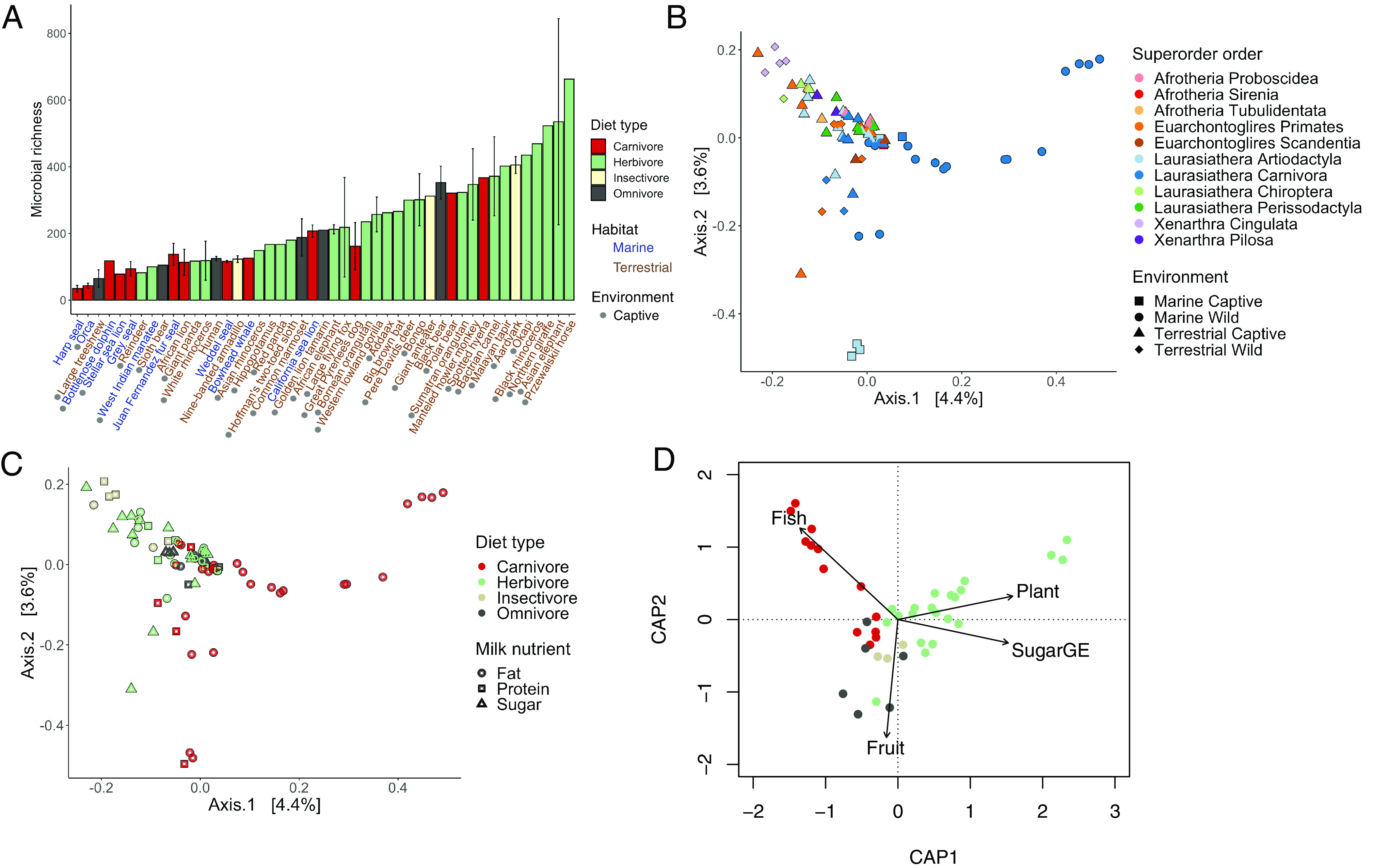
Milk microbiome structure explained by deterministic processes. (A) Captive terrestrial mammals had greater bacterial richness than captive marine mammals. Bottlenose dolphins displayed in figure as captive (n = 2 captive, n = 1 wild). Herbivores had greater bacterial richness and phylogenetic diversity than carnivores. Mammalian milk microbiome composition covaries with (B) superorder and environment, as well as (C) diet type and milk nutrient category as show with principal coordinate analysis of Bray–Curtis distances. (D) Milk microbiome composition changed in a linear manner with host consumption of fish, plants, and fruit, and the amount of sugar GE in milk (based on Bray–Curtis composition measure and distance-based linear models).
