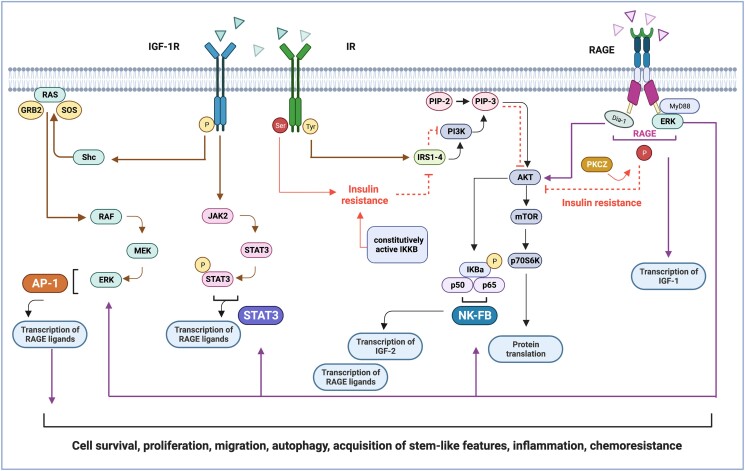
Figure 5.
Signaling cross-talk between IIGFs and RAGE. Schematic representation of the translational mediators shared by IIGFs and RAGE which culminate in NF-κB, activator protein -1 and STAT3-mediated gene transcription. Ligands belonging to IIGFs induce receptor phosphorylation at tyrosine level (in yellow). The subsequent engagement of IRSs (1-4) promotes the activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK cascades, toward gene transcription and protein translation. IIGFs-mediated signals also involve the recruitment of NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 pathway, which in turn promote the transcription of RAGE ligands (like S100A7), as well as the transcription of IIGFs ligands (like IGF-2). During insulin resistance, insulin receptor phosphorylation at serine (in red), rather than tyrosine residues, inhibits the activation of IRS-1/PI3K/AKT pathway, thus repressing insulin-mediated signals. RAGE activation contributes to insulin resistance through the engagement of PKC-ζ (PKCZ), which directly inhibits IRS-1/PI3K/AKT signaling. RAGE activation also induces the transcription of IGF-1, thus increasing its availability. Parallel, an increased phosphorylation of IGF-1R is evidenced upon activation of the AGE/RAGE axis, thereby amplifying IIGFs signaling. Abbreviations: AKT, protein kinase B; AP-1, activator protein 1; Dia1, diaphanous-related formin 1; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GRB2, growth factor receptor–bound protein 2; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IKBa, I kappa b kinase type a; IKKB, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta; IR, insulin receptor; JAK, Janus kinase; IR-A, insulin receptor isoform A, IR-B, insulin receptor isoform B; IRS, insulin-receptor substrate; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKC-ζ, protein kinase c zeta type; PIP-2, phosphatidyl inositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP-3, phosphatidylinositol (3-5)-trisphosphate; RAS, rat sarcoma family of proteins; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma protein; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end products; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; shc, Src homology/collagen protein; SOS, son of sevenless protein.