FIGURE 1.
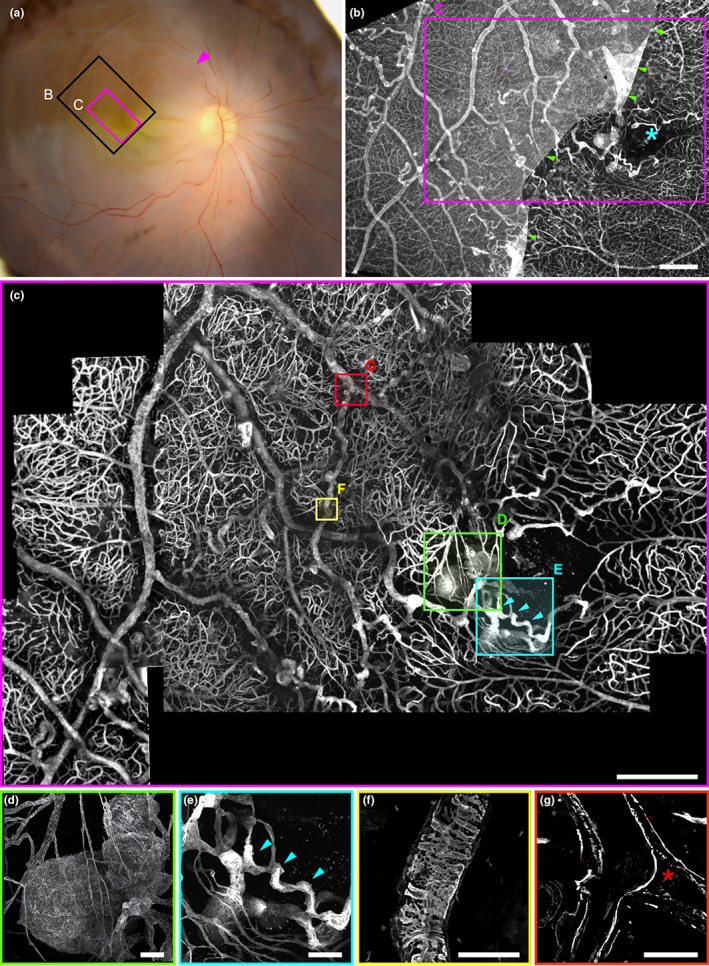
(a) Post‐mortem fundus photograph of the sample superimposed on the area examined by microscopy. Arrowhead indicates the presumed site of occlusion; areas shown in (b) and (c) are boxed in black and magenta, respectively. (b) Epifluorescence imaging. The blue asterisk marks the foveal avascular zone. The presence of the inner limiting membrane, stained by anticollIV antibodies, partially attached to the macula, explained the lower contrast on the left of the image. (c) Confocal microscopy of the foveal area; localisations of panels (d–g) are figured. (d) 3D view of the parafoveal TelCap. Note the presence of surrounding string‐like (nonfunctional) capillaries. (e) 3D view of the parafoveal collateral vein (blue arrowheads). (f) Abnormal collagen IV labeling over a vein. (g) A venous confluence with one branch occluded (red asterisk). Scale bars: (b, c): 500 μm, d–g: 50 μm.
