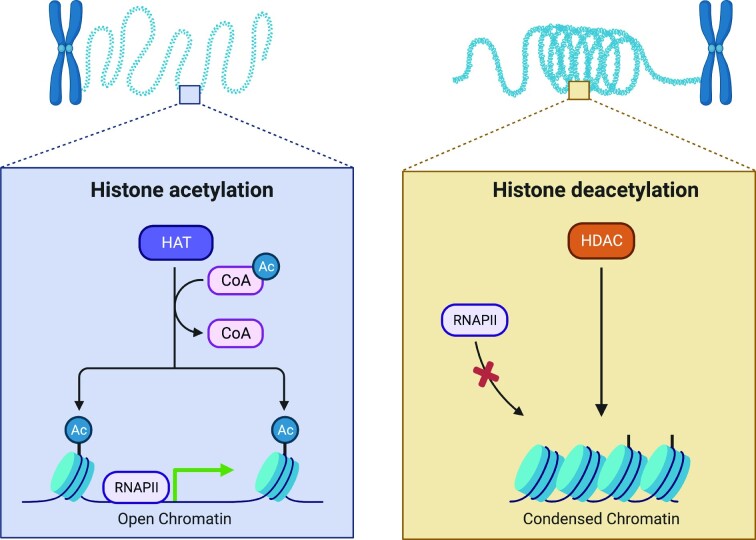
Figure 1.
Histone acetylation and deacetylation. The acetylation of histone lysine residues involves the covalent attachment of an acetyl group to the ε-position of the lysine side chain, which creates an open chromatin structure that is more permissible for gene transcription. Lysine deacetylation involves the removal of the acetyl group, leading to a more compacted chromatin structure that is less accessible for active gene expression. Created with BioRender.com.