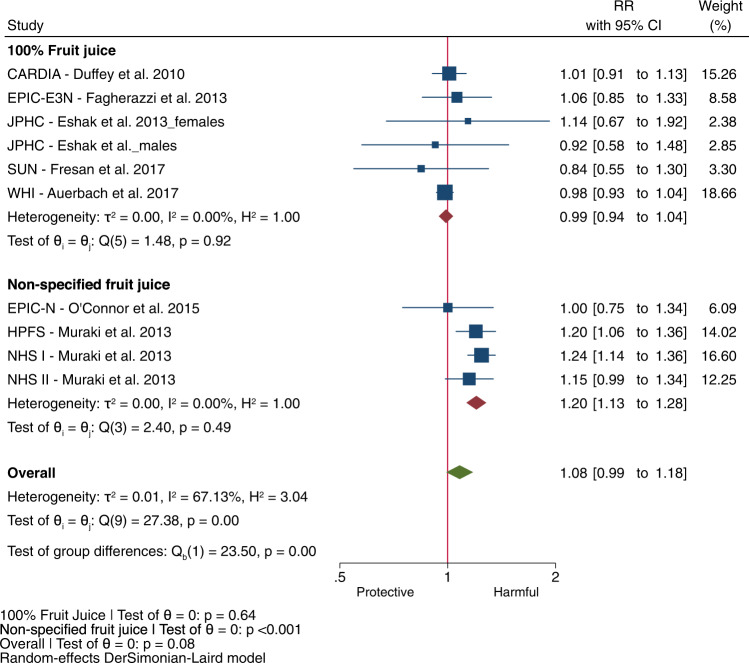
Fig. 1. Relation of fruit juice with incident type 2 diabetes by fruit juice definition (100% fruit juice or non-specified fruit juice) for every increase in serving (250 mL) in adults in 10 prospective cohort comparisons identified by EFSA.
Effect estimates for each subgroup and overall effect are represented by the diamonds. Data are expressed as relative risks with 95% confidence intervals using the generic inverse variance method with DerSimonian-Laird random-effects model. Inter-study heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochrane Q statistic and quantified using the I2 statistic, with significance set at P < 0.10 and I2 ≥ 50% considered to be evidence of substantial heterogeneity. Subgroup differences were tested using the standard Q-test with significance set at P < 0.10. CARDIA Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults Study, CI confidence interval, EPIC-E3N European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition-Etude Epidémiologique auprès des femmes de la Mutuelle Générale de l’Education National, EPIC-N European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition-Norfolk, HPFS Health Professionals Follow-up Study, JPHC Japan Public Health Centre-based Prospective Study, NHS Nurses’ Health Study, RR relative risk, SUN Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra, WHI Women’s Health Initiative.