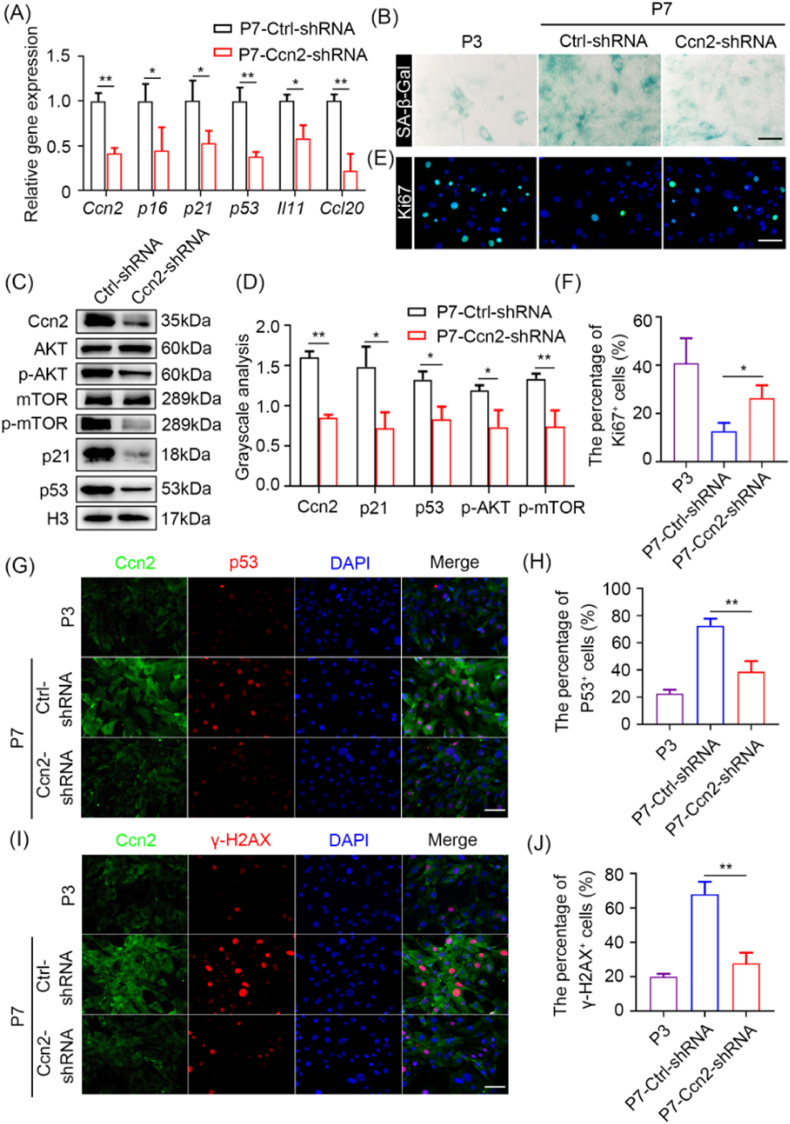
Fig. 7.
Ccn2 plays an important role in cell senescence. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of senescence-related genes in ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. (B) SA-β-gal staining of P3 MEFs, ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (C) Western blot analysis of the levels of Ccn2, AKT, p-AKT, mTOR, p-mTOR, p21 and p53 in ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. (D) Grayscale statistical analysis of Ccn2, p21 and p53 relative to H3, p-AKT relative to AKT, p-mTOR relative to mTOR. (E) Immunofluorescence analysis of Ki67 in P3 MEFs, ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (F) Quantification of the percentage of Ki67 positive MEFs. (G) Immunofluorescence analysis of Ccn2 and p53 in P3 MEFs, ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (H) Quantification of the percentage of p53 positive MEFs. (I) Immunofluorescence analysis of Ccn2 and γ-H2AX in P3 MEFs, ctrl P7 MEFs and Ccn2 knockdown P7 MEFs. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (J) Quantification of the percentage of γ-H2AX positive MEFs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 3. Student's t-test: ns, not significance; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.