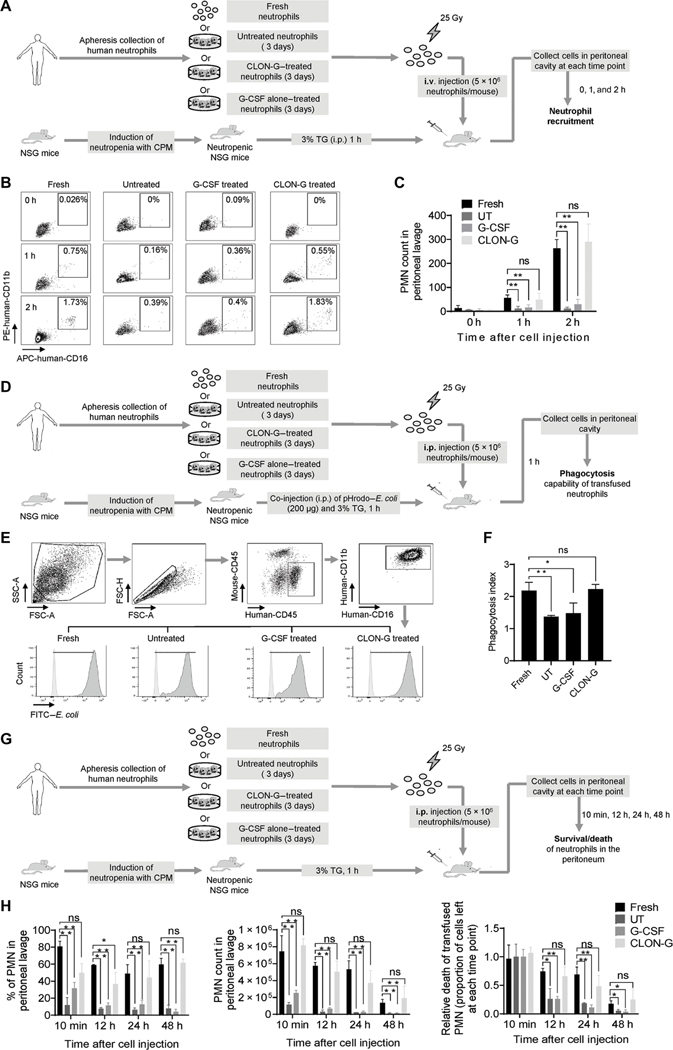
Fig. 8. Pretreatment with CLON-G prolongs half-life of transfused human neutrophils in vivo in NSG mice.
(A) Experimental scheme for assessing the recruitment of transfused fresh, untreated, G-CSF alone–treated, and CLON-G–treated human neutrophils in NSG mice in a mouse peritonitis model. Human neutrophils were isolated from granulocyte apheresis concentrates as described in Fig. 6 and cultured in the presence of indicated compounds for the indicated time period. Peritonitis in neutropenic NSG mice was induced with 3% TG. i.v., intravenous. (B) Recruitment of transfused human neutrophils to inflamed peritoneal cavities was assessed by flow cytometry. (C) The total recruited human neutrophil number is presented as total cell number multiplied by the percentage of transfused human neutrophils in peritoneal cavities as calculated by flow cytometry. All data are presented as means ± SD of four experiments. **P < 0.001 compared to the corresponding “Fresh neutrophils” group. (D) Experimental scheme for assessing the in vivo phagocytosis capability of transfused human neutrophils in NSG mice in the peritonitis model. (E) Engulfment of pHrodo–E. coli by transfused human neutrophils was analyzed by flow cytometry. FSC-H, forward scatter height; FSC-A, forward scatter area; SSC-A, side scatter area. (F) The phagocytosis index was calculated for indicated samples as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) fold increase (MFI of treated or untreated human neutrophils at 1 hour/ MFI of the corresponding human neutrophils at time 0). All data are presented as means ± SD of four experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 compared to Fresh neutrophils group. ns, no significant difference (P > 0.05). (G) Experimental scheme for assessing the in vivo death rate of transplanted fresh, untreated, G-CSF alone–treated, and CLON-G–treated human neutrophils in NSG mice in a mouse peritonitis model. (H) The percentage of human neutrophils in peritoneal cavities was calculated by flow cytometry. The number of human neutrophils left at each indicated time point was calculated as total cell number multiplied by the percentage of human neutrophils in the peritoneal cavity. Relative death of transplanted human neutrophils was calculated as the proportion of cells left at each time point. All data are presented as means ± SD of four experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 compared to the corresponding Fresh neutrophils group. ns, no significant difference (P > 0.05).