Figure 8.
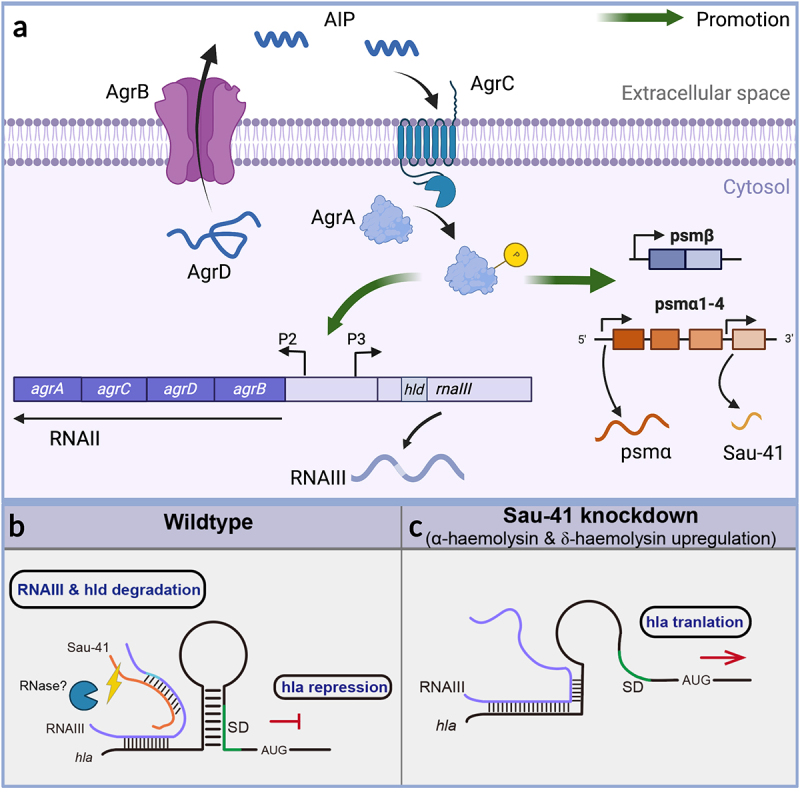
(a) Schematic of the S. aureus Agr system. The AgrD precursor undergoes maturation and export through AgrB, generating the AIP signal. Once the AIP concentration reaches a specific threshold, it triggers the activation of the AgrC-AgrA two-component system. Phosphorylated AgrA then initiates transcription from the P2 promoter, leading to the regulation of auto-feedback. In addition, AgrA facilitates the transcription of RNAIII via the P3 promoter. Furthermore, AgrA enhances the transcription of the psmα and psmβ operons, which encode PSM peptides. Sau-41 is transcribed from the psmα operon. (b-c) the mechanism of Sau-41 in regulating S. aureus virulence. (b) Wild-type: Sau-41 binds with RNAIII thus repressing the expression of α-haemolysin(hla). The Sau-41 and RNAIII complex was probably degraded by RNase III, thus down-regulating the expression of δ-toxin (hld). (c) When Sau-41 was knockdown, RNAIII was preserved and could interact with hla 5’UTR. hla expression was upregulated because its SD sequence was available for ribosome binding.
