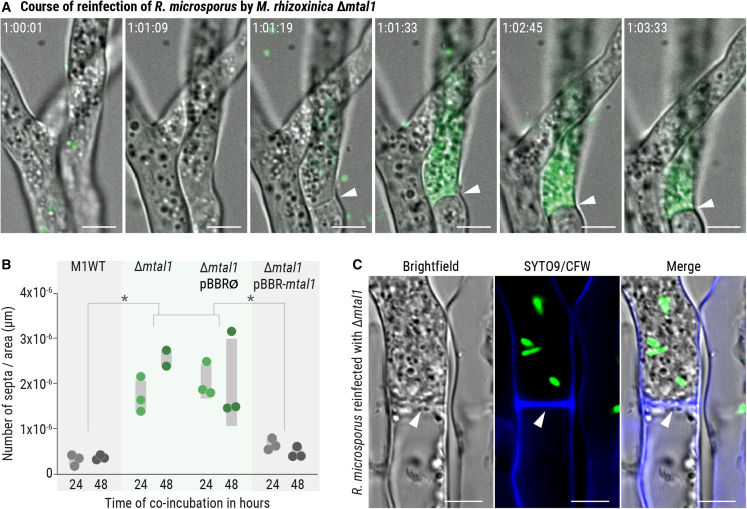
Figure 4.
Formation of septa after colonization of R. microsporus by MTAL1-deficient M. rhizoxinica
(A) Course of colonization of R. microsporus by M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1. Colonization was monitored over time using fluorescence microscopy (Video S1). Arrowheads indicate the formation of septa. Scale bars: 5 μm.
(B) The number of septa per hyphal area (in μm) was calculated for M. rhizoxinica wild type (M1WT), M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1, M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR∅, and M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR-mtal1. Dots represent three independent replicates (n = 3 biological replicates) ± SEM (gray bars). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (∗p < 0.05, Data S4A–S4D).
(C) Fluorescence microscopy images showing the formation of septa (indicated by an arrow head) in R. microsporus (blue stain) colonized by M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 (green). Scale bars: 5 μm. See also Figures S5A and S5B.