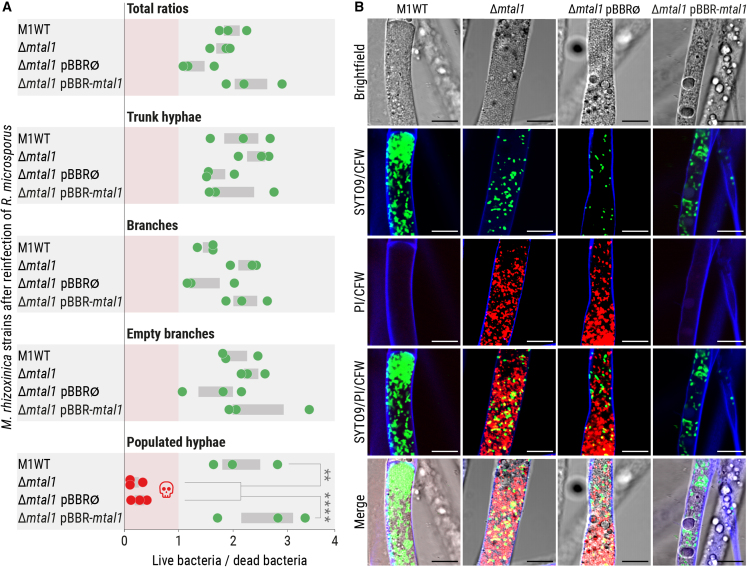
Figure 5.
Viability test of M. rhizoxinica following colonization of R. microsporus
(A) Viability of M. rhizoxinica wild type (M1WT), M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1, M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR∅, and M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR-mtal1 inside R. microsporus after 72 h of co-cultivation in a bacterial-fungal interaction (BFI) device. Co-cultures were stained with LIVE/DEAD BacLight fluorescent dyes inside the BFI device. Following fluorescence microscopy, the integrated density was calculated for both live (SYTO9-stained) and dead bacteria (propidium iodide-stained [PI]) using Fiji. The ratio (live/dead) was plotted for the total number of bacteria and for each individual type of hyphae. Dots represent three independent replicates (n = 3 biological replicates) ± SEM (gray bars). One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test (∗∗p < 0.002, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Data S5).
(B) Microscopic images of R. microsporus colonized by M. rhizoxinica wild type (M1WT), M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1, M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR∅, or M. rhizoxinica Δmtal1 pBBR-mtal1 stained with LIVE/DEAD BacLight fluorescent dyes. Scale bars: 10 μm. See also Figure S5C.