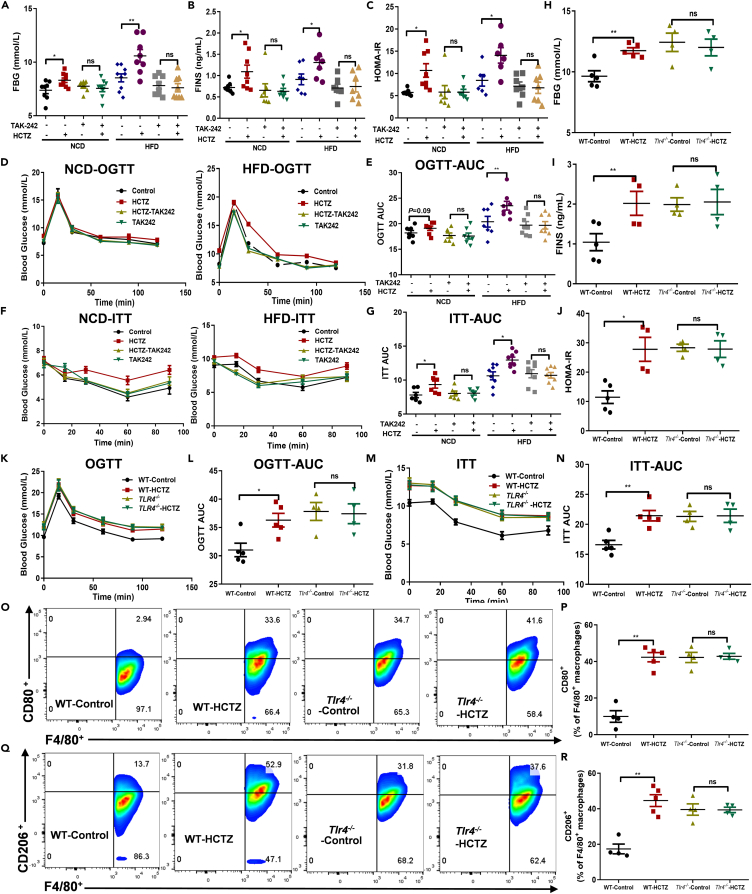
Figure 6.
The macrophage polarization and inflammatory effects of HCTZ were dependent on TLR4 signaling
(A–N) FBG (A), FINS (B), HOMA-IR (C), OGTT (D), OGTT-AUC (E), ITT (F), and ITT-AUC (G) in mice treated with the TLR4 inhibitor TAK-242 (n = 6–8 per group); FBG (H), FINS (I), HOMA-IR (J), OGTT (K), OGTT-AUC (L), ITT (M), and ITT-AUC (N) in WT or Tlr4−/− mice treated with HCTZ or vehicle control (n = 4–5 per group). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(O and P) (O) Representative CD80 staining of hepatic F4/80+ macrophages of WT or Tlr4−/− mice treated with HCTZ or vehicle control.
(P) Flow cytometry analysis of CD80+-F4/80+ macrophages (n = 4–5 per group). ∗∗p < 0.01. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
(Q and R) (Q) Representative CD206 staining of hepatic F4/80+ macrophages of WT or Tlr4−/− mice treated with HCTZ or vehicle control.
(R) Flow cytometry analysis of CD206+-F4/80+ macrophages (n = 4–5 per group). ∗∗p < 0.01. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.