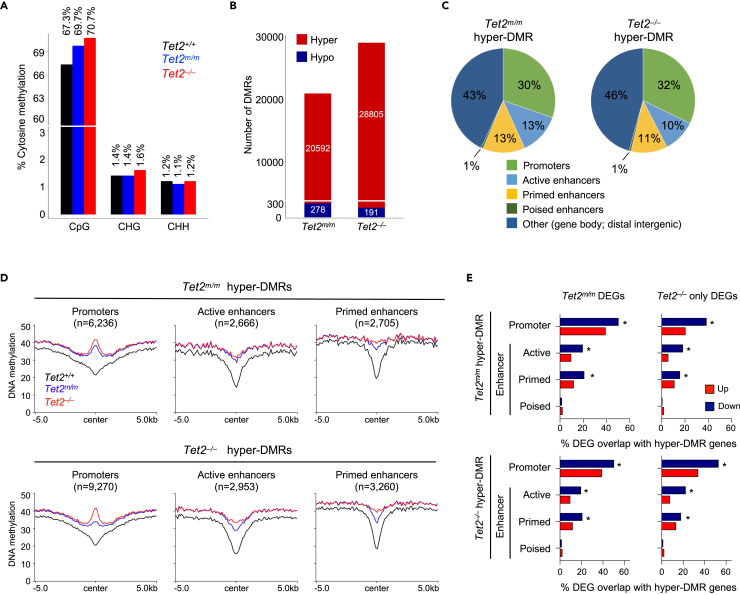
Figure 3.
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation in Tet2m/m and Tet2−/− ESCs reveals hypermethylation of gene regulatory elements
(A) Genome-wide percent CpG, CHG and CHH methylation levels in Tet2+/+, Tet2m/m, and Tet2−/− ESCs measured by whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS).
(B) Quantification of differentially methylated regions (DMRs = >5 CpGs, methylation difference >20%, and FDR <0.05) in Tet2m/m and Tet2−/− ESCs compared to wildtype ESCs. Note that the majority of DMRs are hypermethylated in both cell types.
(C) Assignment of hypermethylated (hyper-) DMRs in Tet2m/m and Tet2−/− ESCs to genomic regions. Note that the majority of DMRs are at promoters and active or primed enhancers.
(D) Profile plots of DNA methylation levels at hyper-DMRs located at promoters and enhancers in Tet2m/m and Tet2−/− ESCs.
(E) Percent of DEGs in Tet2m/m and Tet2−/− ESCs that overlap with hyper-DMR-associated genes. Note the significant association between downregulated genes and hypermethylated promoters, active and primed enhancers (∗p < 0.05 by hypergeometric test).