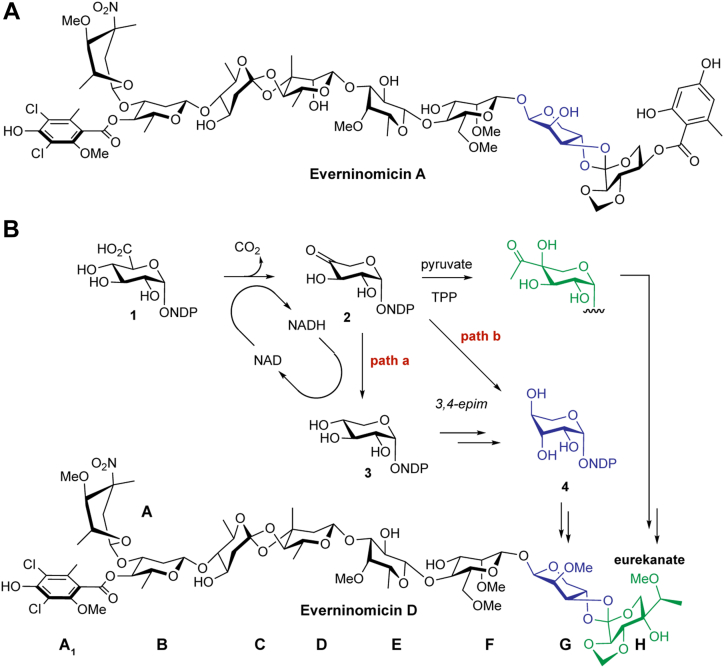
Figure 1.
Everninomicin A and D.A, the structure of everninomicin A, the original clinical candidate, rendered to approximate the conformation adopted in the ribosome-bound co-crystal structure. B, the structure of everninomicin D, showing the potential biosynthesis to both the G- and H-ring sugars. Path a follows other known NDP-D-glucuronic acid (1) decarboxylases in the formation of NDP-D-xylose (3) with subsequent enzyme(s) catalyzing the epimerization reactions at C-3” and C-4”. Path b suggests that the decarboxylase could also function as an C-3” epimerase and inverting C-4” reductase, leading directly to NDP-L-lyxose (4).