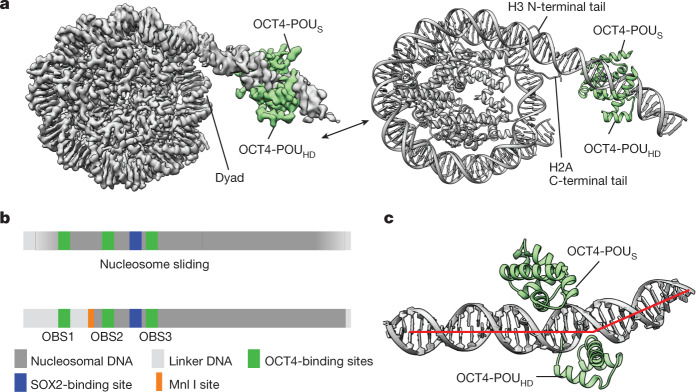
Fig. 1. OCT4 binds to the nucleosome at the exposed DNA site.
a, A composite cryo-EM map (left) and the structural model (right) of human OCT4 (green) bound to a nucleosome (grey) assembled with a 182-bp DNA fragment from the LIN28B locus. b, Schematic representation of DNA positioning on the LIN28B nucleosome. Binding sites for OCT4 (OBS1, OBS2 and OBS3) and SOX2, and the Mnl I restriction site are shown. The nucleosome is ‘fuzzy’ as the DNA adopts multiple positions due to spontaneous sliding (top). OCT4 binding stabilizes DNA at a defined position on the nucleosome (bottom). c, Close-up view of OCT4 (green) bound to the nucleosomal DNA (grey; the red line shows the path of the DNA helix axis), showing the kink in the linker DNA introduced by OCT4-POUHD.