Extended Data Fig. 9. Histone modifications modulate OCT4 and SOX2 cooperativity on various human DNA.
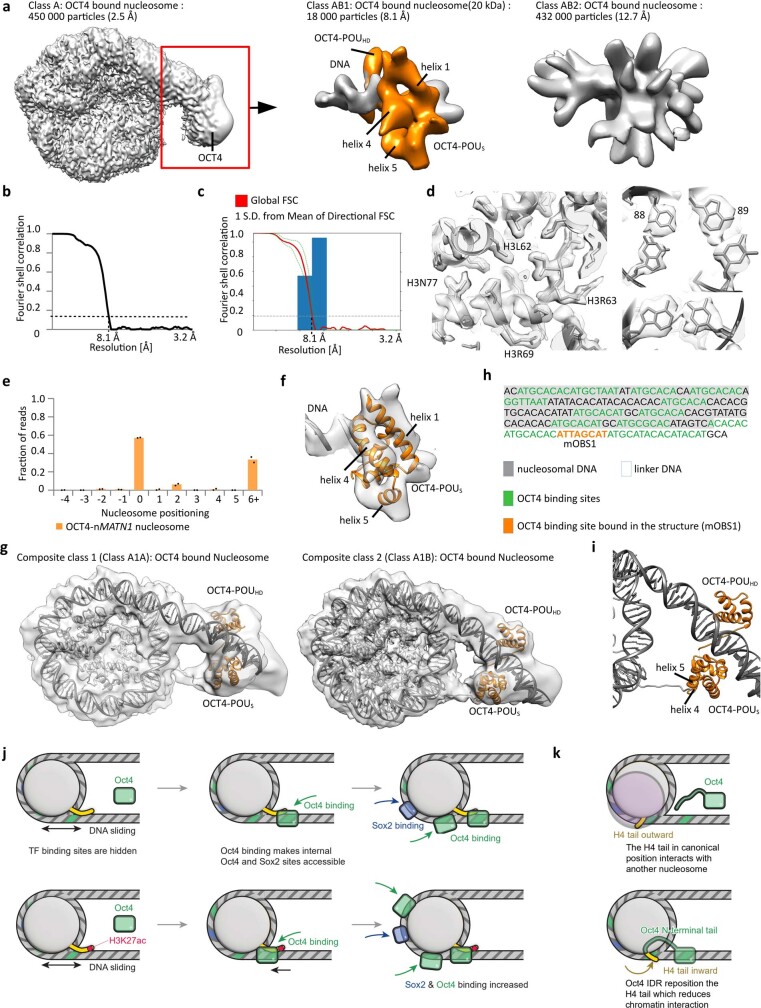
a) Cryo-EM map of OCT4 region from the OCT4_nucleosome complex from Fig. 8g). Focused classification and refinements improved the resolution of this 20 kDa fragment to 8.1 Å. b) Fourier shell correlation (FSC) curve showing the resolution of the map in a). c) Directional FSC plot showing uniform resolution in all directions. d) Representative regions showing map quality and fit of the model are shown for the nucleosome with bound OCT4. Right: bases in the DNA are well resolved. e) Quantification of sequencing of Mnase I digested OCT4-bound nMATN1 nucleosomes. The y-axis shows fraction of nucleosome size reads starting at defined position, the x-axis shows position of the first base pair relative to the most abundant position (0 as observed in the structure). Data are mean and spread of 2 independent experiments. f) The model of the OCT4 bound to DNA (Extended Data Fig. 2g) was refined into the cryo-EM map. The representative region showing map quality and fit of the model is shown. g) Cryo-EM models of OCT4 bound to the nMATN1 nucleosome containing 186bp of DNA at 2.2-5.6 Å resolution for two most dominant conformations. h) DNA sequence and schematic representation showing nMATN1 DNA positioning on the OCT4_nucleosome complex. Potential OCT4 binding sites are labeled in green. OCT4 binding site occupied in the structure is labeled in orange. i) Close-up views of the nucleosome entry/exit site showing interaction of the OCT4_POUS domain with the H3 N-terminal tail. Ribbon representation shows OCT4_POUS helix 4 and helix 5 interacting with histone H3 N-terminal tail. j) In LIN28B nucleosome OCT4 (light green) and SOX2 (light blue) binding sites are wrapped around the histone octamer. LIN28B nucleosomes are mobile, and nucleosome sliding transiently exposes the OCT4 binding site 1 (green), which leads to binding of OCT4 (green box). OCT4 binding (green box) traps DNA in a more defined position, which exposes internal OCT4 and SOX2 binding sites (blue). OCT4 bound to the OBS1 interacts with the histone H3 tail. H3K27ac modifies this interaction leading to DNA movement towards the histone octamer, which exposes internal OCT4 and SOX2 sites even more, leading to increased binding. k) The canonical H4 tail conformation (yellow, facing outward) favors inter-nucleosome interactions by interacting with the acidic patch of neighboring nucleosomes. These interactions are essential for chromatin compaction. OCT4 DNA binding domain binds linker DNA whereas disordered activation domain binds H4 near the H4 tail. This repositions the H4 tail to an inward conformation that reduces inter-nucleosome interactions in chromatin.