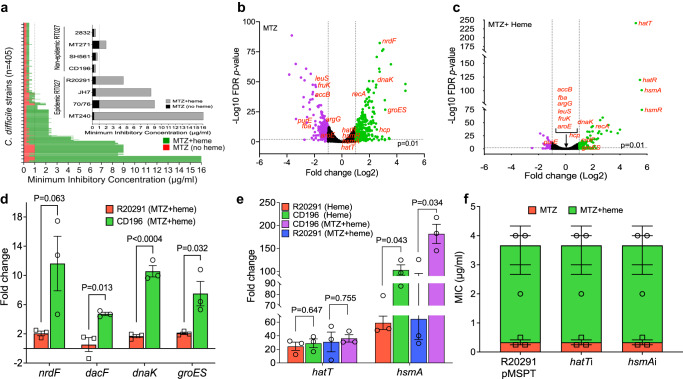
Fig. 1. Heme attenuates cellular toxicity of metronidazole (MTZ) in epidemic C. difficile strains.
a Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of MTZ were determined against global clinical isolates of C. difficile (n = 405) in the presence and absence of heme. Isolates with heme-dependent MTZ resistance exhibited ≥4-fold higher MICs in BHI agars containing heme, compared to agars without heme. An MTZ MIC of 1 μg/ml (dashed line) was found to be associated with poor clinical outcomes58, although the EUCAST resistance breakpoint is 2 μg/ml. Inset illustrates selected RT027 epidemic and non-epidemic strains that are resistant or susceptible to MTZ in heme, respectively. Non-epidemic RT027 were defined as previously described24 (i.e., lacking fluoroquinolone resistance SNPs in gyrase A and large transposons found in epidemic RT027). MICs were from two biological replicates with two technical replicates. Transcriptome response of epidemic R20291 (OD600 nm ≈ 0.2) exposed for 30 min to MTZ (2 μg/ml) in the absence (b) and presence (c) of heme (5 μg/ml). The volcano plots indicate differentially expressed genes and their statistical significance; the purple and green dots indicate significantly downregulated and upregulated genes, respectively; red-highlighted genes are cell stress-responsive and metabolic genes whose expression were altered by MTZ but were attenuated by heme. The RNA-seq is based on two biological replicates, as the third replicate was rejected in FastQC due to poor quality. Pearson correlation of R2 = 0.94 in Supplementary Fig. 2b shows RNA-seq transcriptional changes were validated by qPCR (three biological replicates). In (b) and (c), differential gene expression was determined with edgeR, an RNA-seq analysis tool with default statistical analysis of false discovery rate (FDR) ≤ 0.01 and Log2 fold change set to ≥1; output p values for each gene were converted to negative logarithm (−Log10) and plotted against Log2-fold change in Graphpad prism 9.4.1. d Transcriptional response of epidemic R20291 and non-epidemic CD196 to MTZ (2 μg/ml) in the presence of heme (5 μg/ml). qPCR analysis of transcription patterns of genes indicative of MTZ toxicity demonstrates heme is not protective for non-epidemic CD196. e Transcriptional analysis of heme sensing/detoxifying genes hatT and hsmA in heme with or without MTZ, indicate that CD196 and R20291 both highly express these genes, as determined by qPCR. Data from (d) and (e) were statistically analyzed in Graphpad prism 9.4.1 by two-tailed multiple unpaired t test with correction for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Šídák method and alpha set to 0.05; data in each plot were from three biological replicates. f Heme sensing and detoxifying systems do not mediate heme-dependent MTZ resistance. In R20291, silencing hatT or hsmA had no effect on heme-dependent resistance, indicating that these genes are unlikely to contribute to heme-dependent resistance; anti-sense RNA to hatT or hsmA was cloned into vector pMSPT and induced by 64 ng/ml of anhydrotetracycline; qPCR indicated hatT mRNA decreased by ~7-fold (i.e., −7.21 ± 1.95) and hsmA by ~18-fold (i.e., −18.46 ± 10.66). Data in (d), (e), and (f) are plotted as mean ± standard error of mean.