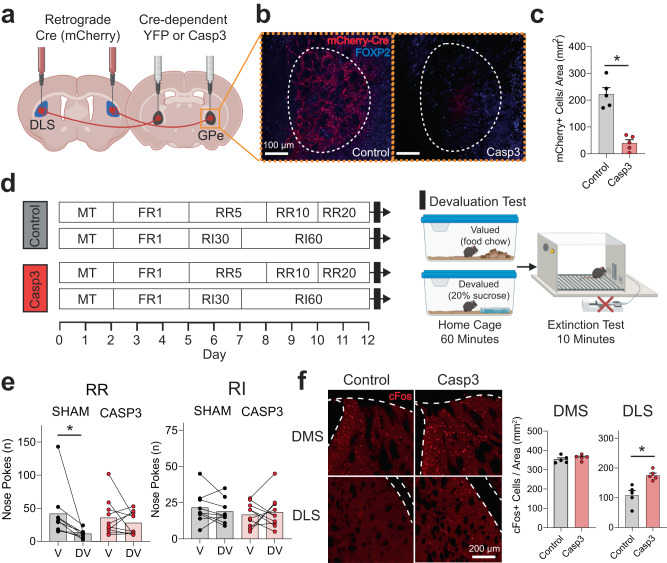
Fig. 4. Effects of Caspase 3 (casp3)-dependent ablation of external globus pallidus (GPe) arkypallidal neurons on goal-directed and habitual-seeking.
a Schematic of virus injections for Cre-dependent ablation of GPe arkypallidal neurons. b Representative GPe images of sham control and caspase mice (Scale: 100 µm) from n = 5 mice/group. c Caspase mice showed a significant reduction of mCherry-positive neurons in the GPe (t = 6.90, p = 0.001). n = 5/group. d Operant RR and RI behavior schedules in sham control and caspase mice to establish goal-directed and habitual seeking, respectively. e RR-trained (Goal-directed) sham mice reduced nose poke responses in the devalued state, confirming goal-directed behavior (p = 0.0039). However, caspase mice showed no changes in nose poke responses between valued and devalued states, typical of habitual behavior (p = 0.73). No differences in nose poke rates between the valued and devalued state for RI-trained sham (p = 0.38) and caspase mice (p = 0.83) indicated habitual reward-seeking. n = 10 mice/group. f Representative IHC images of cFos expression in the dorsomedial (DMS) and dorsolateral (DLS) striatum for sham and casp3 mice (Scale: 200 µm). GPe arkypallidal neuron ablation increased the number of cFos-positive cells in the DLS (t = 3.99, p = 0.004), but not DMS (t = 1.02, p = 0.34). n = 5 mice/group. Two-tailed t tests were used for (c, f). Wilcoxon test was used for (e). Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. See Supplementary Table 2 for full statistical information. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. (a, d) were created with BioRender.com.